Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

An overview of substrate stiffness guided cellular response and its applications in tissue regeneration - ScienceDirect
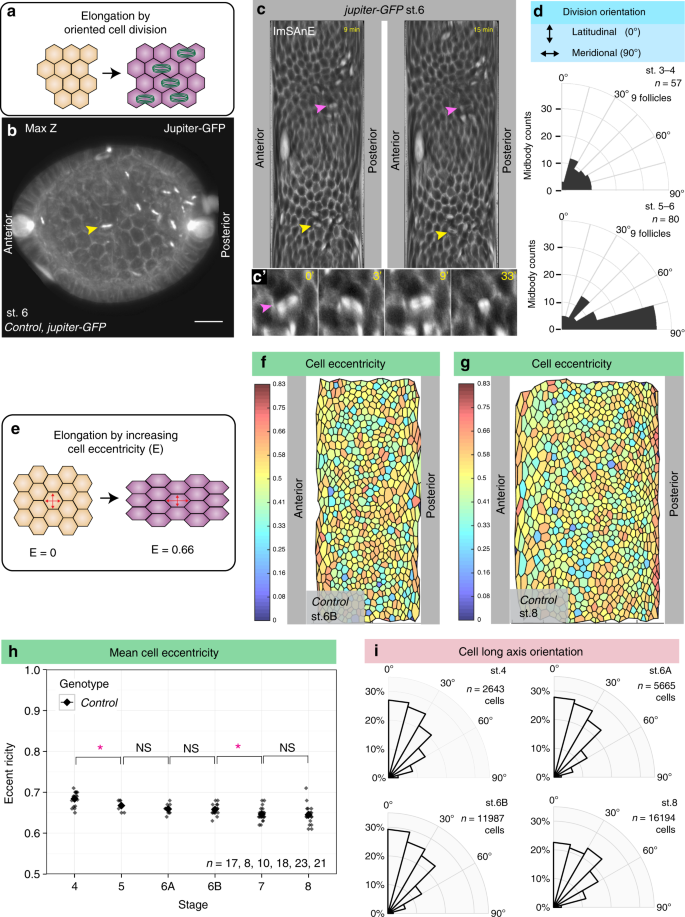
Extracellular matrix stiffness cues junctional remodeling for 3D tissue elongation

Biomechanics of cells and subcellular components: A comprehensive review of computational models and applications - Wang - 2021 - International Journal for Numerical Methods in Biomedical Engineering - Wiley Online Library

An overview of substrate stiffness guided cellular response and its applications in tissue regeneration - ScienceDirect

Stiffness transitions in new walls post-cell division differ between Marchantia polymorpha gemmae and Arabidopsis thaliana leaves
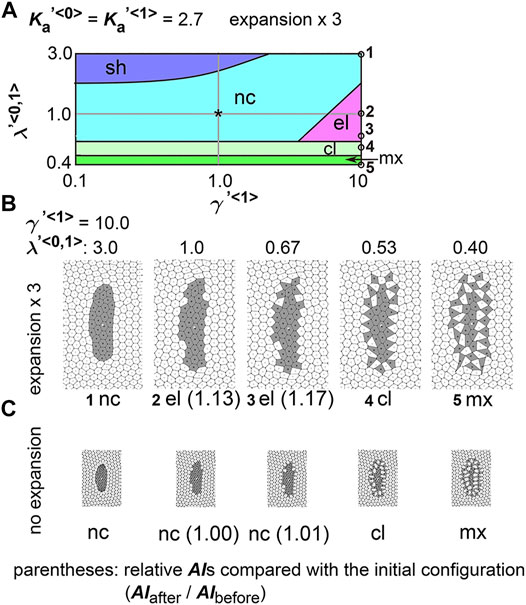
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface
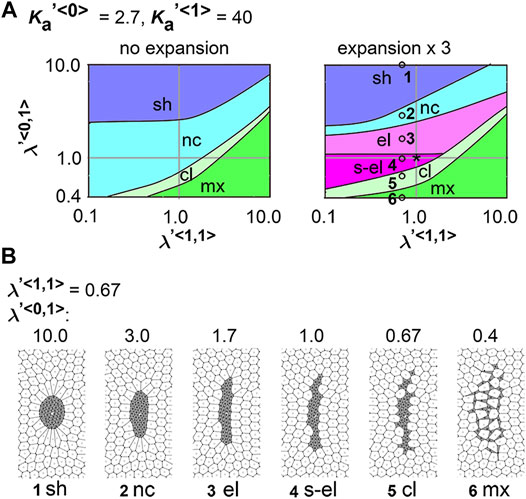
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface

Synthetic fibrous hydrogels as a platform to decipher cell–matrix mechanical interactions

Effect of matrix stiffness on cell height (A) Cell height was
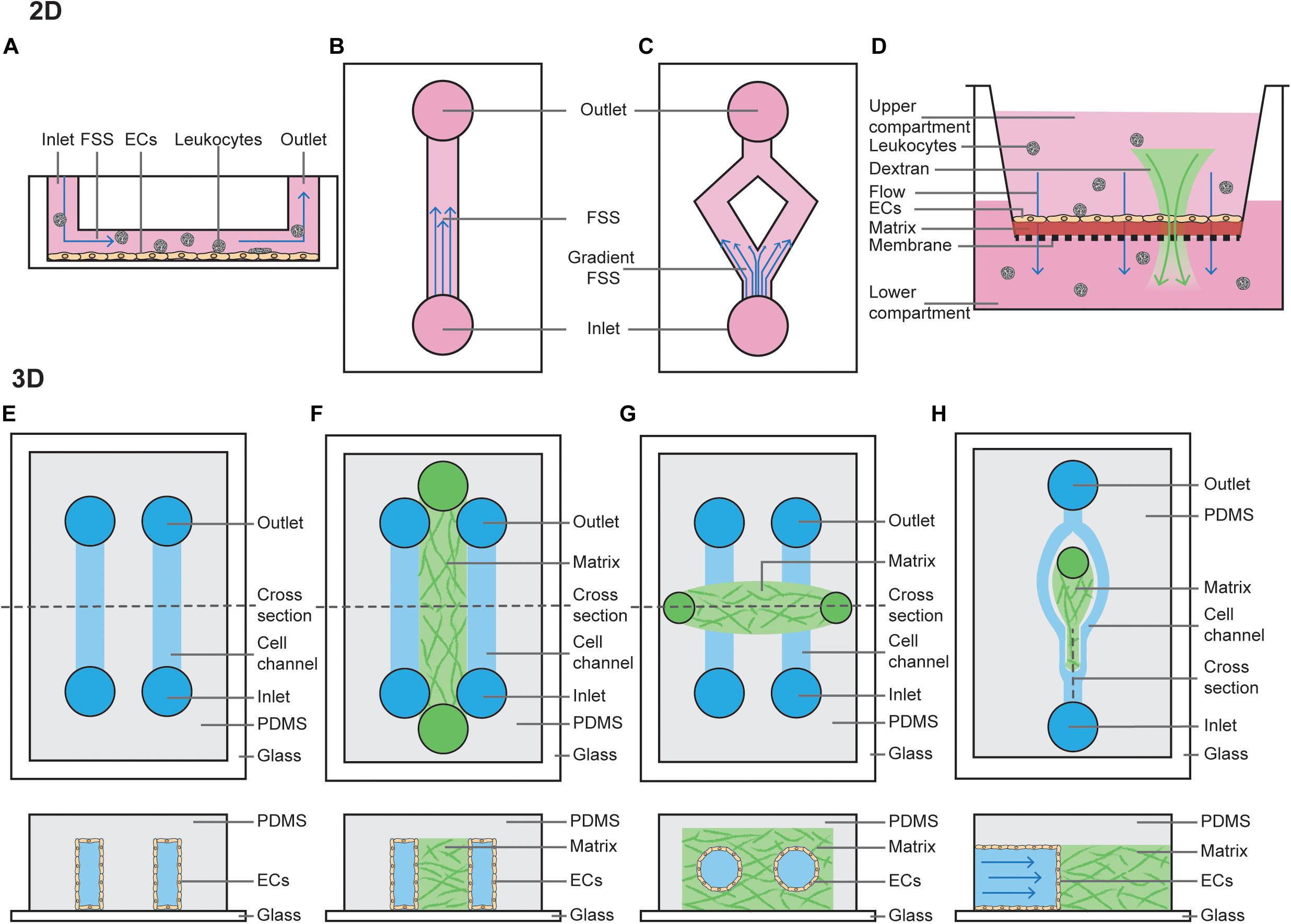
Frontiers The Importance of Mechanical Forces for in vitro Endothelial Cell Biology

Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface

Macrophages modulate stiffness-related foreign body responses through plasma membrane deformation
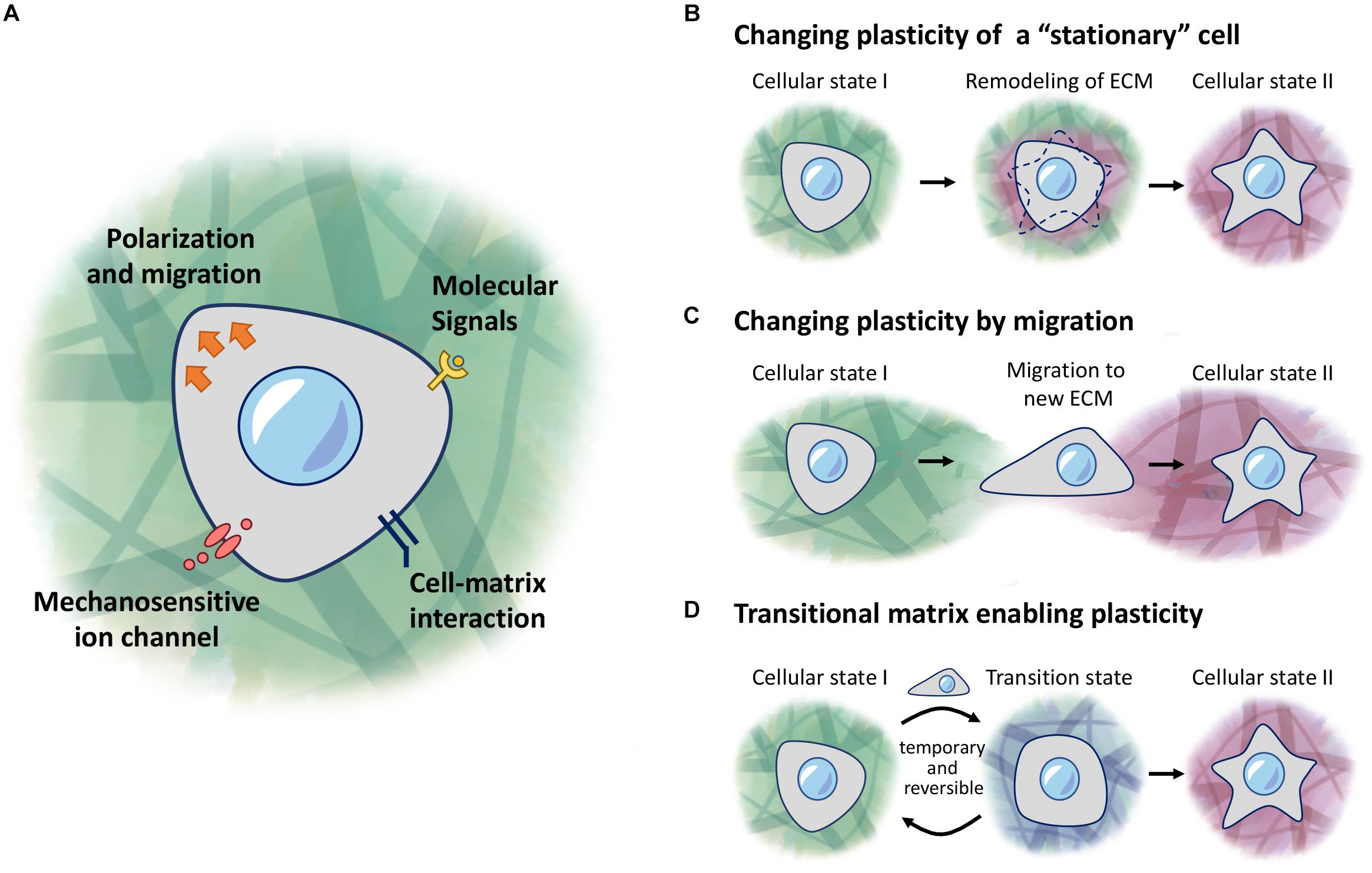
Frontiers Extracellular Matrix and Cellular Plasticity in Musculoskeletal Development
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







