Urban landscapes and legacy industry provide hotspots for riverine greenhouse gases: A source-to-sea study of the River Clyde - ScienceDirect
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

The comparison of greenhouse gas emissions in sewage treatment

Anthropogenic-estuarine interactions cause disproportionate
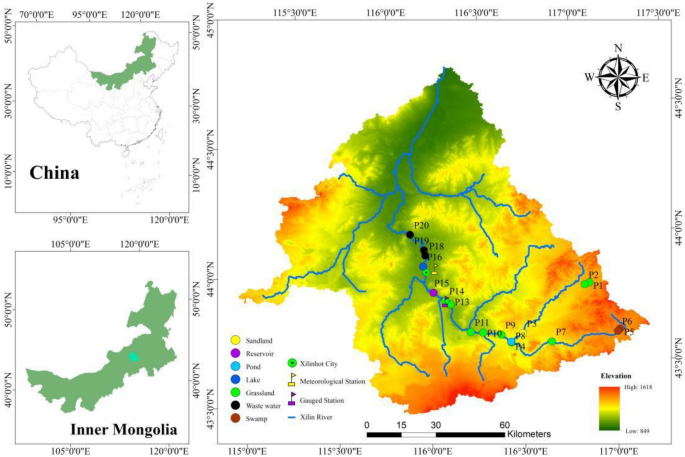
Greenhouse gas emissions from the water–air interface of a

PDF) Anthropogenic-estuarine interactions cause disproportionate

Greenhouse gases in an urban river: Trend, isotopic evidence for
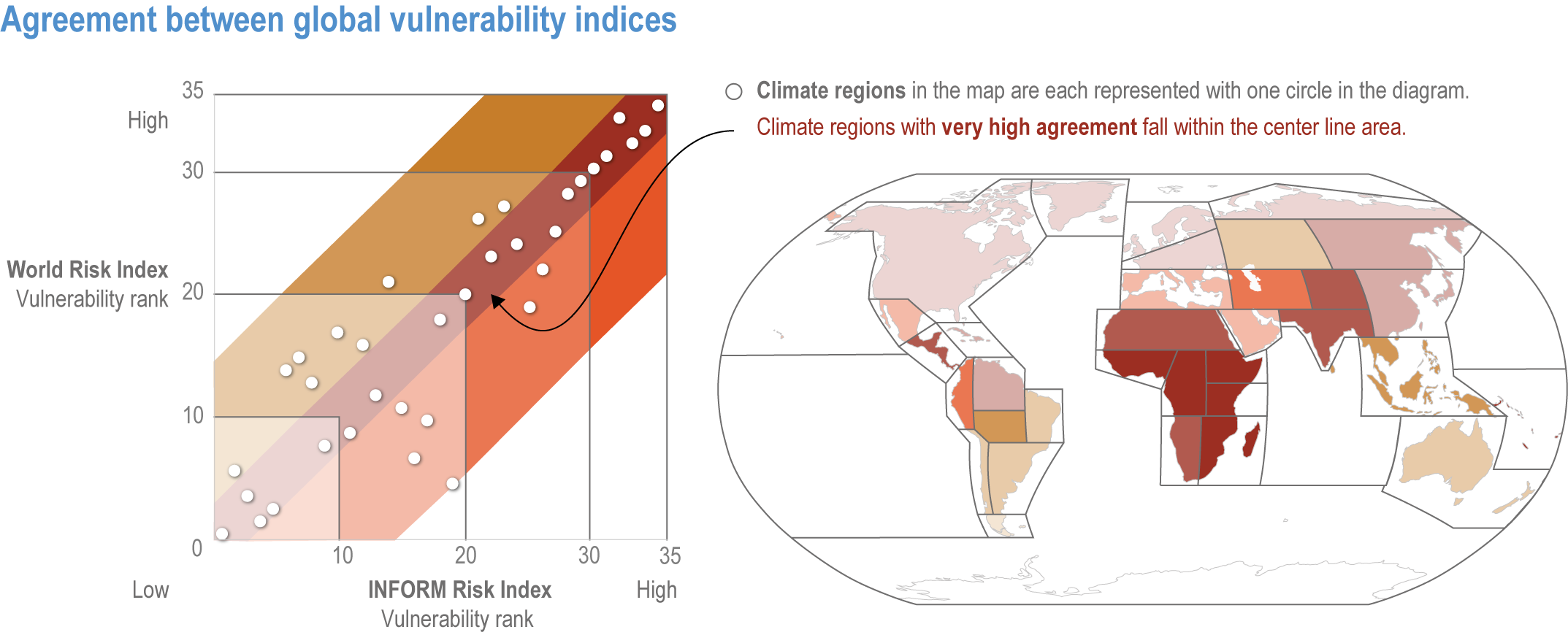
Chapter 8: Poverty, Livelihoods and Sustainable Development
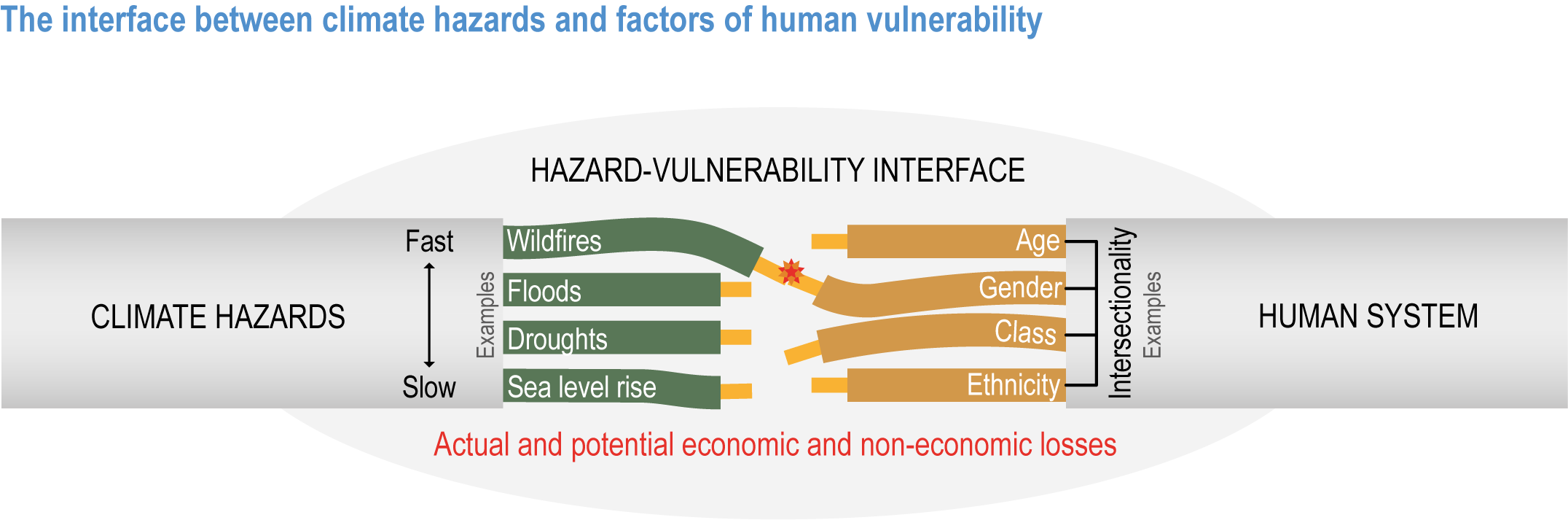
Chapter 8: Poverty, Livelihoods and Sustainable Development

Urban landscapes and legacy industry provide hotspots for riverine

pCO2 and CO2 evasion from two small suburban rivers: Implications

Methane and nitrous oxide concentrations and fluxes from heavily

Anthropogenic-estuarine interactions cause disproportionate

Anthropogenic land use substantially increases riverine CO2

Controls of Land Use and the River Continuum Concept on Dissolved

Water Research, Vol 236, 1 June 2023
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)






