Theorem on Friends and Strangers; Why in Any Party of Six People, Either at Least Three of Them Are Mutual Friends, or at Least Three of Them Are Mutual Strangers
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Let’s take a look at Alice first. To her, each one of the other five (Bob, Carol, Dave, Ellen, and Frank) is either a friend or a stranger. Suppose Bob, Dave, and Frank are friends to Alice, and…

Solved Counting: product rule, sum rule, inclusion-exclusion
How to prove: at a party of six people either there are three mutual acquaintances or there are three mutual strangers - Quora

Theorem on Friends and Strangers; Why in Any Party of Six People, Either at Least Three of Them Are Mutual Friends, or at Least Three of Them Are Mutual Strangers

Madeline Dawsey--Modular Forms and Ramsey Theory.

Proof by cases example: Three mutual friends/enemies theorem
Ramsey Theory on Facebook - Scientific American Blog Network

SOLVED: Prove this theorem: Among any six people, there exists a group of 3 mutual friends or a group of 3 mutual strangers. (Here friends and strangers are considered symmetric relations, i.e.

Friends and strangers

Friends and strangers

Ramsey's Theorem: Friends and Strangers

Friends and strangers

Friends and strangers
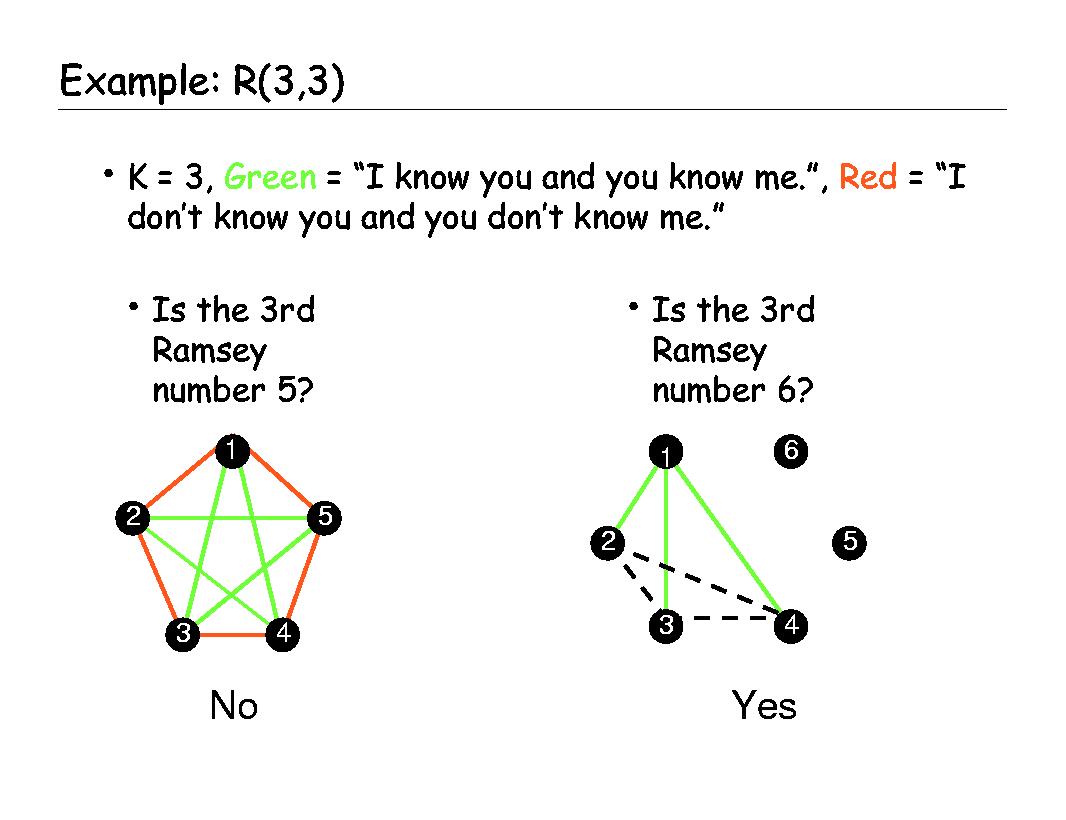
CS290I Lecture notes -- Let's Party
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







