Mosaic CREBBP mutation causes overlapping clinical features of Rubinstein–Taybi and Filippi syndromes
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Figure 1 from Mutations in CKAP2L, the human homolog of the mouse Radmis gene, cause Filippi syndrome.

Mosaic CREBBP mutation causes overlapping clinical features of Rubinstein– Taybi and Filippi syndromes

SciELO - Brasil - Dental anomalies in syndromes displaying hypertrichosis in the clinical spectrum Dental anomalies in syndromes displaying hypertrichosis in the clinical spectrum
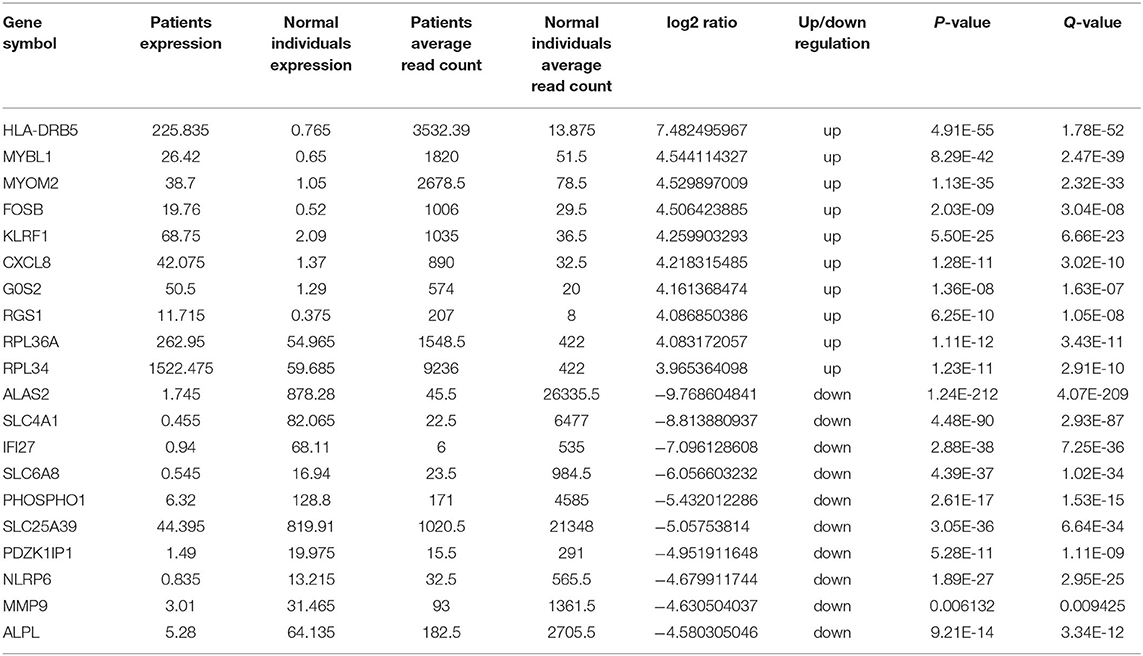
Frontiers Case Report: Low-Level Maternal Mosaicism of a Novel CREBBP Variant Causes Recurrent Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome in Two Siblings of a Chinese Family

Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome in diverse populations - Tekendo‐Ngongang - 2020 - American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A - Wiley Online Library
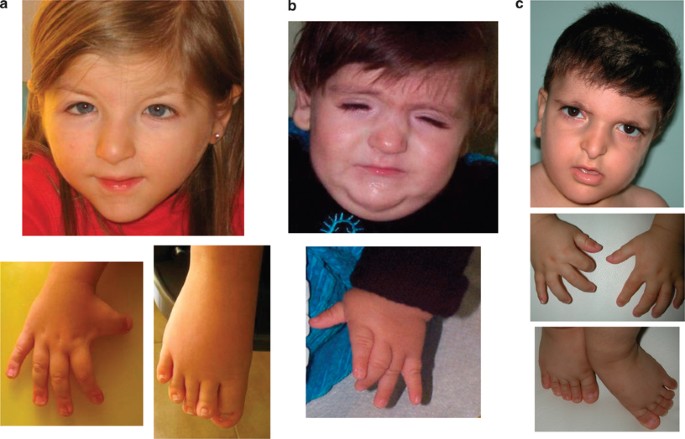
High frequency of copy number imbalances in Rubinstein–Taybi patients negative to CREBBP mutational analysis
PDF) Case Report: Low-Level Maternal Mosaicism of a Novel CREBBP Variant Causes Recurrent Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome in Two Siblings of a Chinese Family

Epigenetic mechanisms of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. - Abstract - Europe PMC

PDF) Clinical exome sequencing identifies novel CREBBP variants in 18 Chinese Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome kids with high frequency of polydactyly

Epigenetic mechanisms of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome. - Abstract - Europe PMC
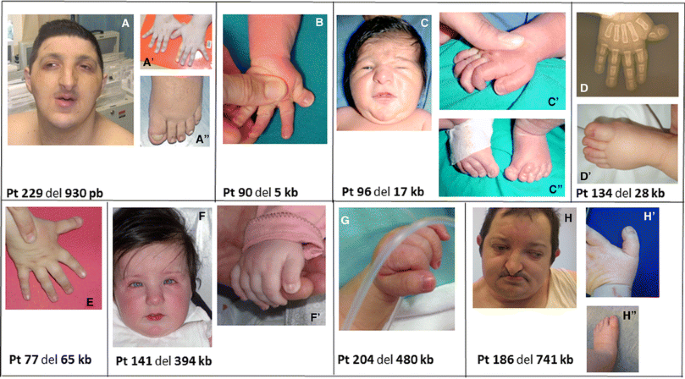
Characterization of 14 novel deletions underlying Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome: an update of the CREBBP deletion repertoire
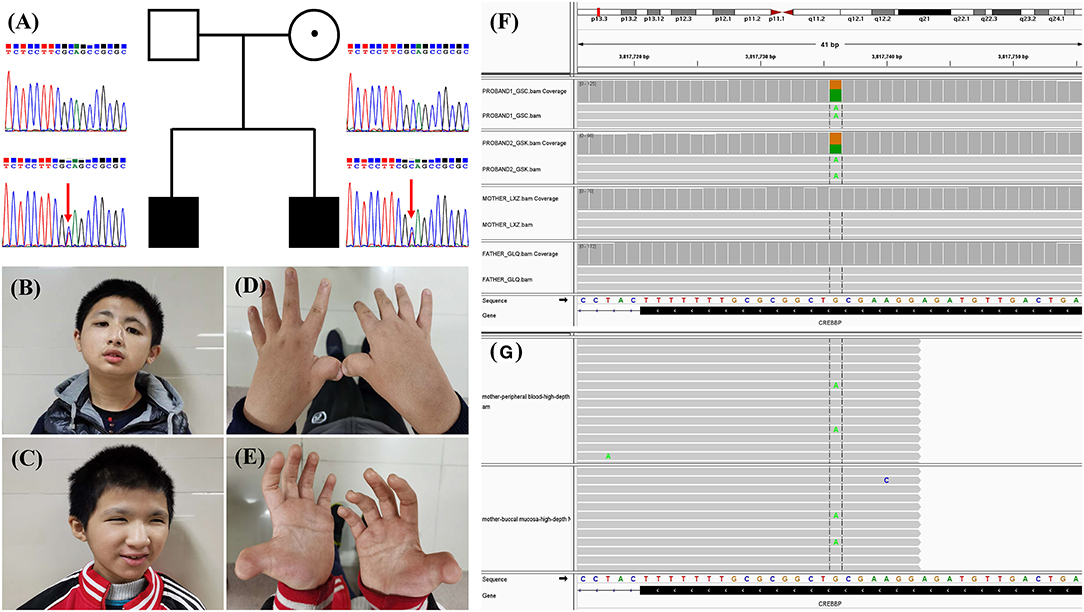
Frontiers Case Report: Low-Level Maternal Mosaicism of a Novel CREBBP Variant Causes Recurrent Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome in Two Siblings of a Chinese Family
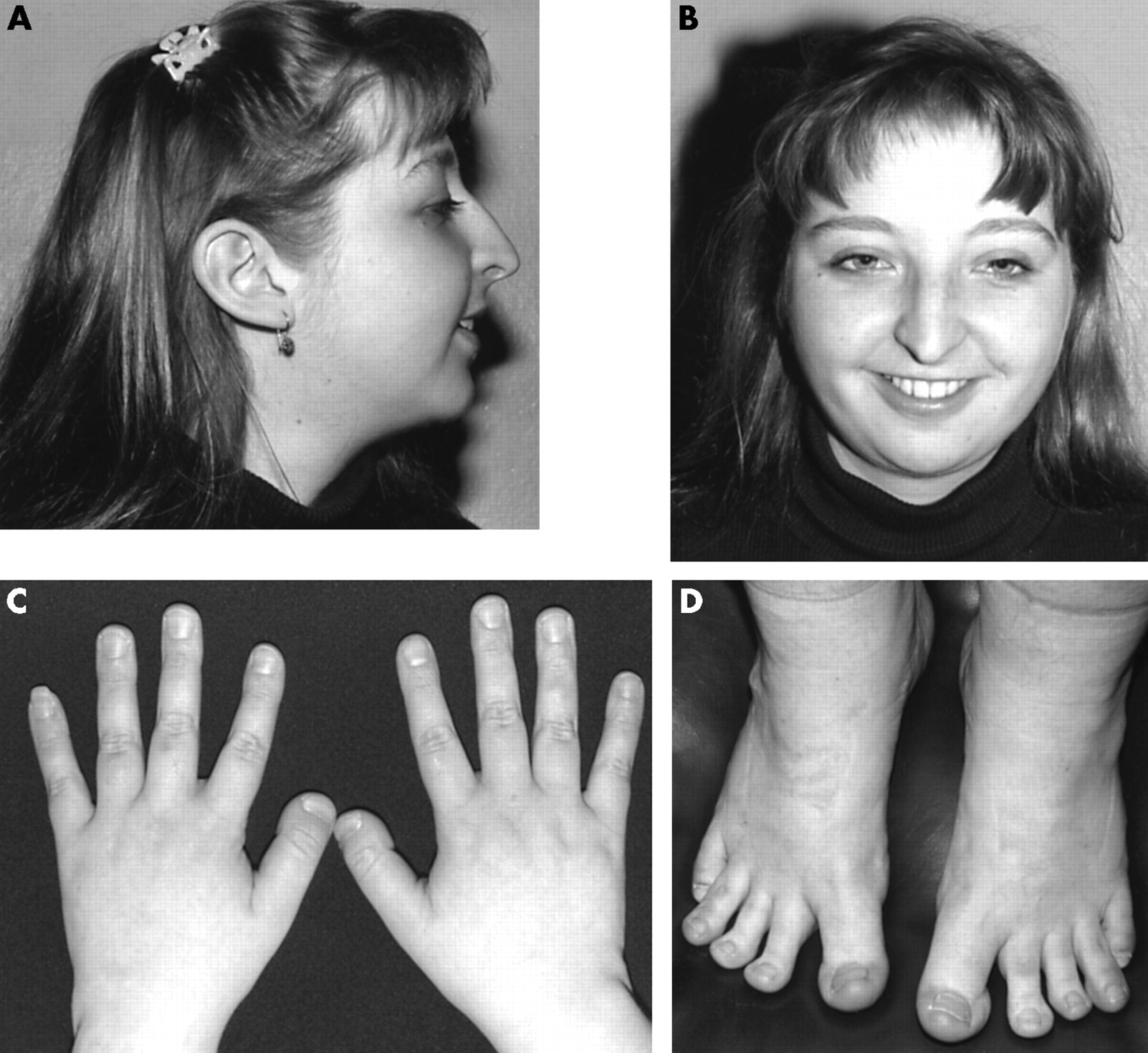
Molecular studies in 10 cases of Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome, including a mild variant showing a missense mutation in codon 1175 of CREBBP
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)