Understanding SARS-CoV-2-Mediated Inflammatory Responses: From
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Currently there is no effective antiviral therapy for SARS-CoV-2 infection, which frequently leads to fatal inflammatory responses and acute lung injury. Here, we discuss the various mechanisms of SARS-CoV-mediated inflammation. We also assume that SARS-CoV-2 likely shares similar inflammatory responses. Potential therapeutic tools to reduce SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammatory responses include various methods to block FcR activation. In the absence of a proven clinical FcR blocker, the use of intravenous immunoglobulin to block FcR activation may be a viable option for the urgent treatment of pulmonary inflammation to prevent severe lung injury. Such treatment may also be combined with systemic anti-inflammatory drugs or corticosteroids. However, these strategies, as proposed here, remain to be clinically tested for effectiveness.

COVID-19

Does infection with or vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 lead to lasting immunity? - The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
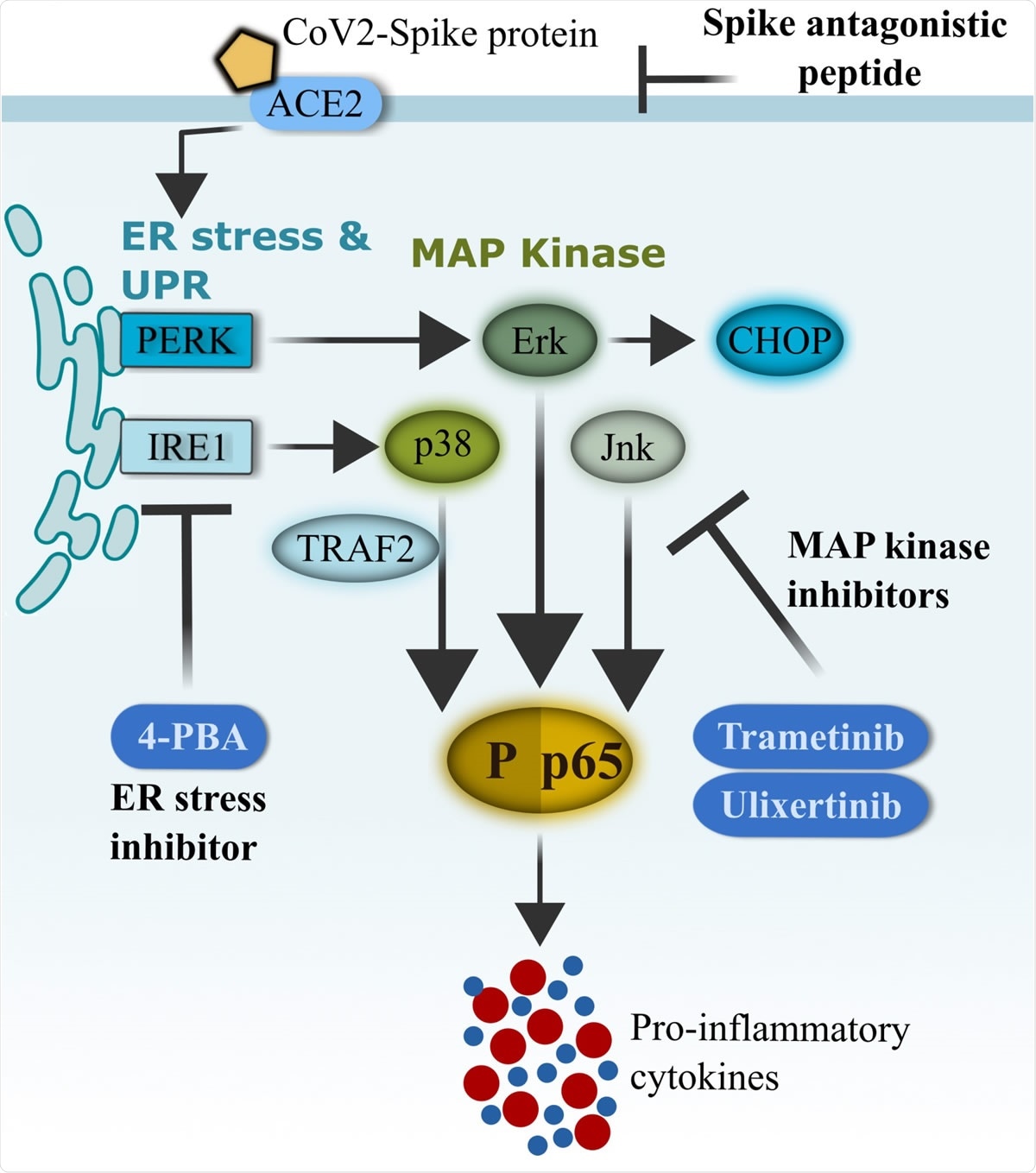
Study confirms SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein promotes a hyper-inflammatory immune response
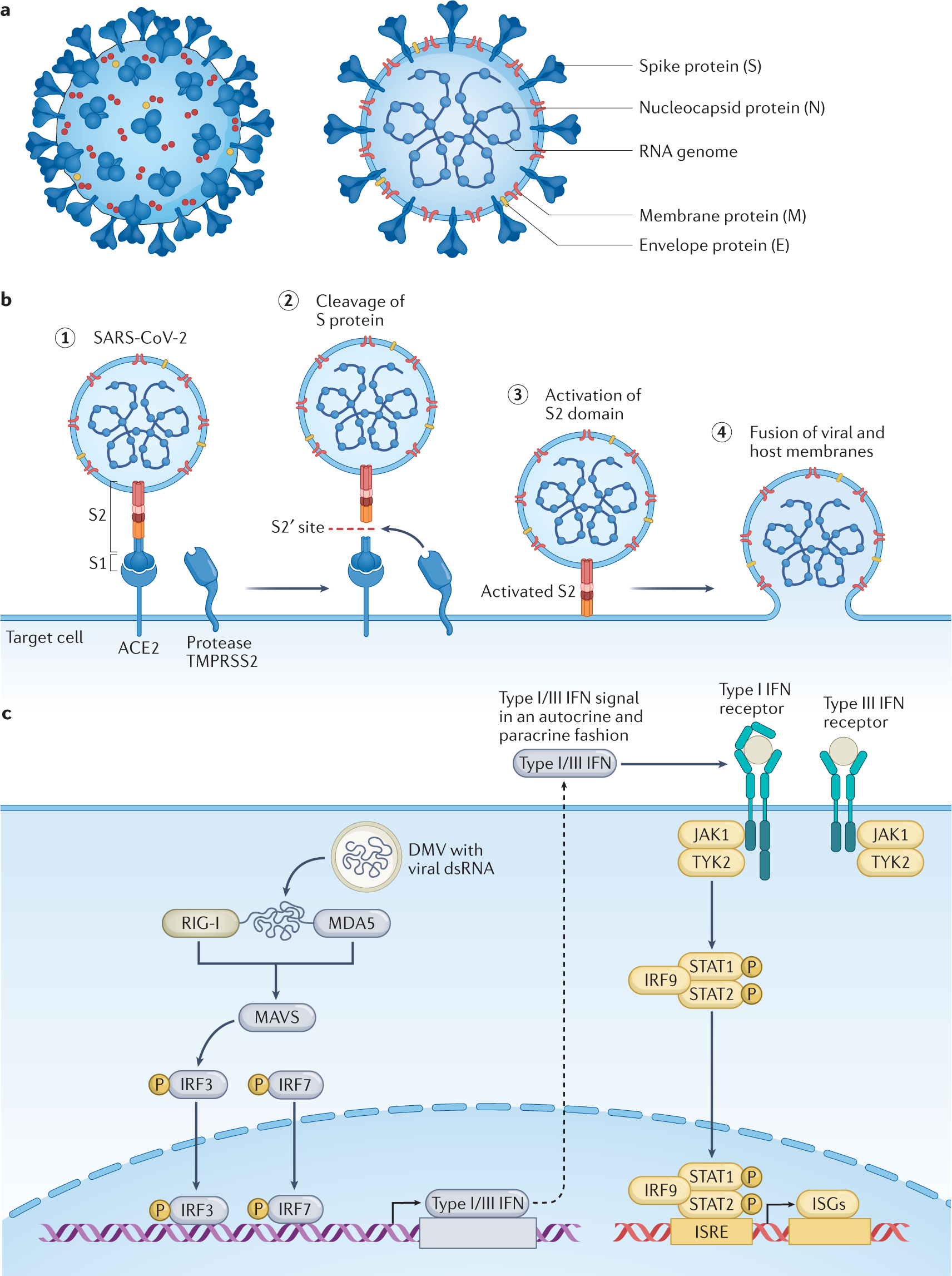
SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis Nature Reviews Microbiology
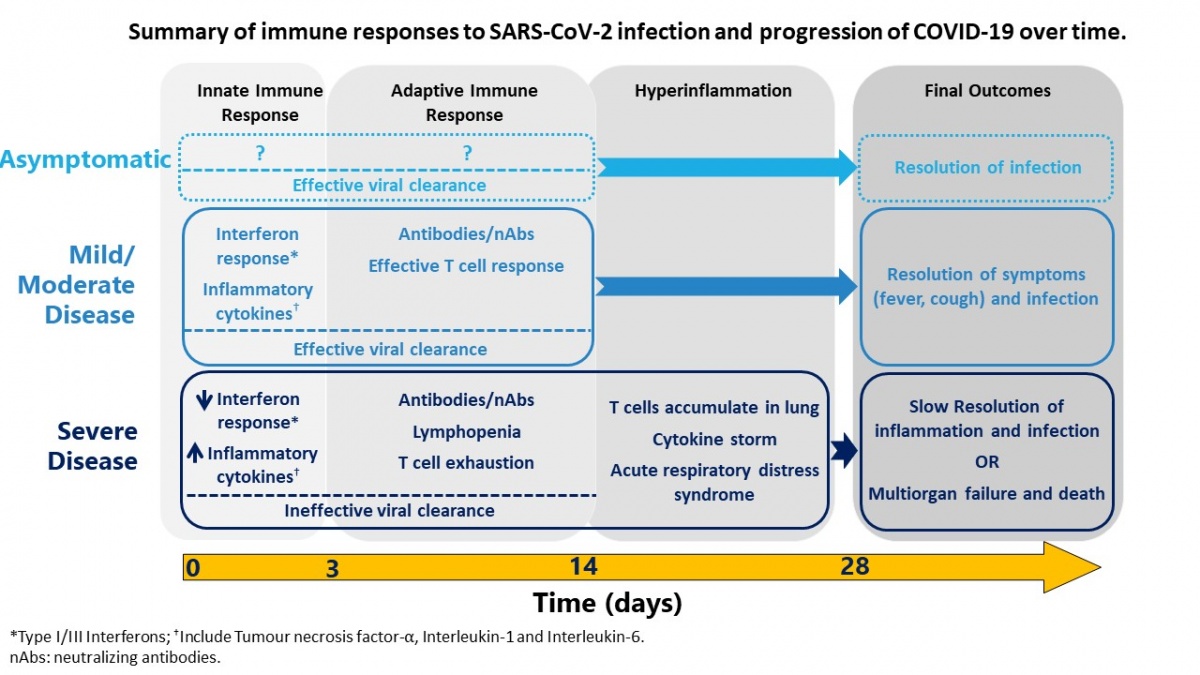
Understanding Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2

What is the role of T cells in COVID-19 infection? Why immunity is about more than antibodies - The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine
Guide to Understanding Th1 and Th2 Cells - Assay Genie

SARS-CoV-2 mediated neuroinflammation and the impact of COVID-19 in neurological disorders - ScienceDirect

COVID-19 therapeutics: Challenges and directions for the future
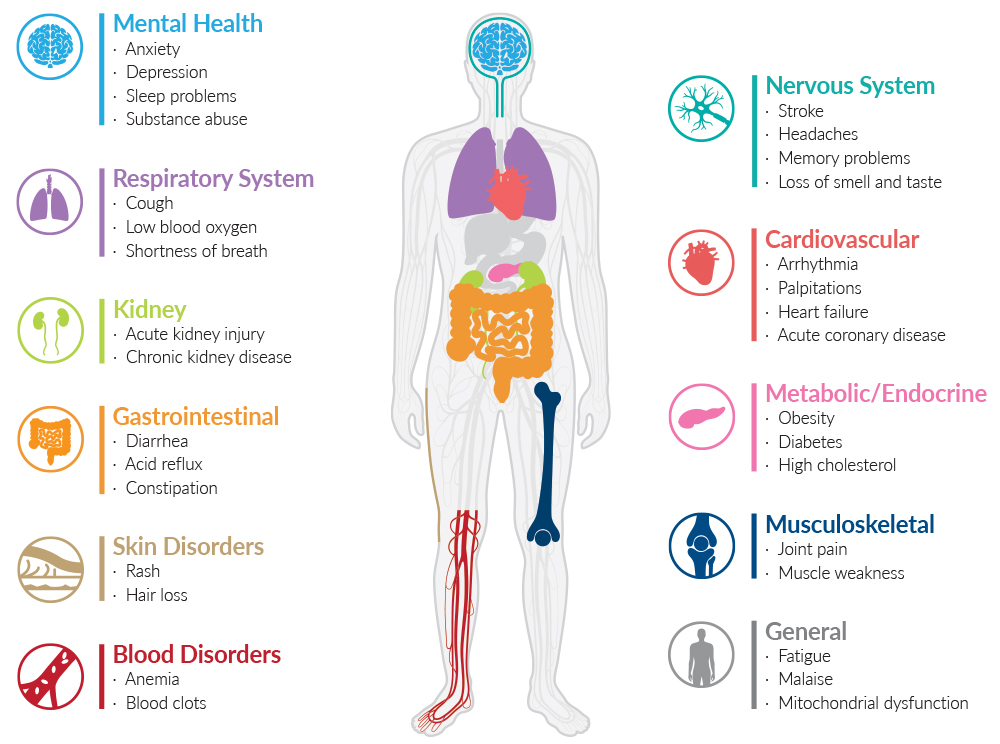
Research Tools for Long COVID Syndrome, News & Announcements
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)




/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2019/G/U/I0iw3DQ5C7Xr2qlOwMAw/pokemon-rumble-rush.jpg)
