CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN Act as Receptors for SARS-CoV-2
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
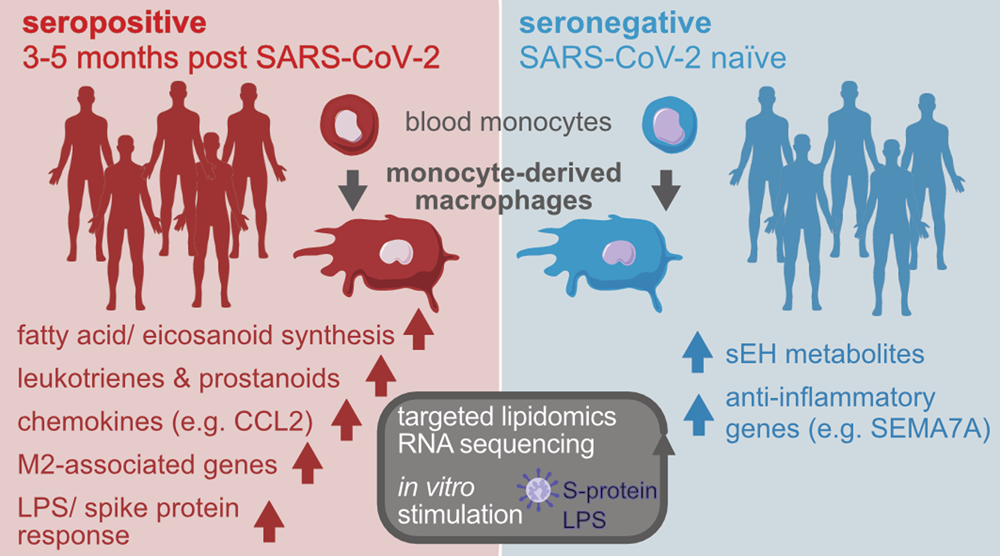
Mild COVID-19 imprints a long-term inflammatory eicosanoid- and chemokine memory in monocyte-derived macrophages

Host genetic factors determining COVID-19 susceptibility and severity - eBioMedicine
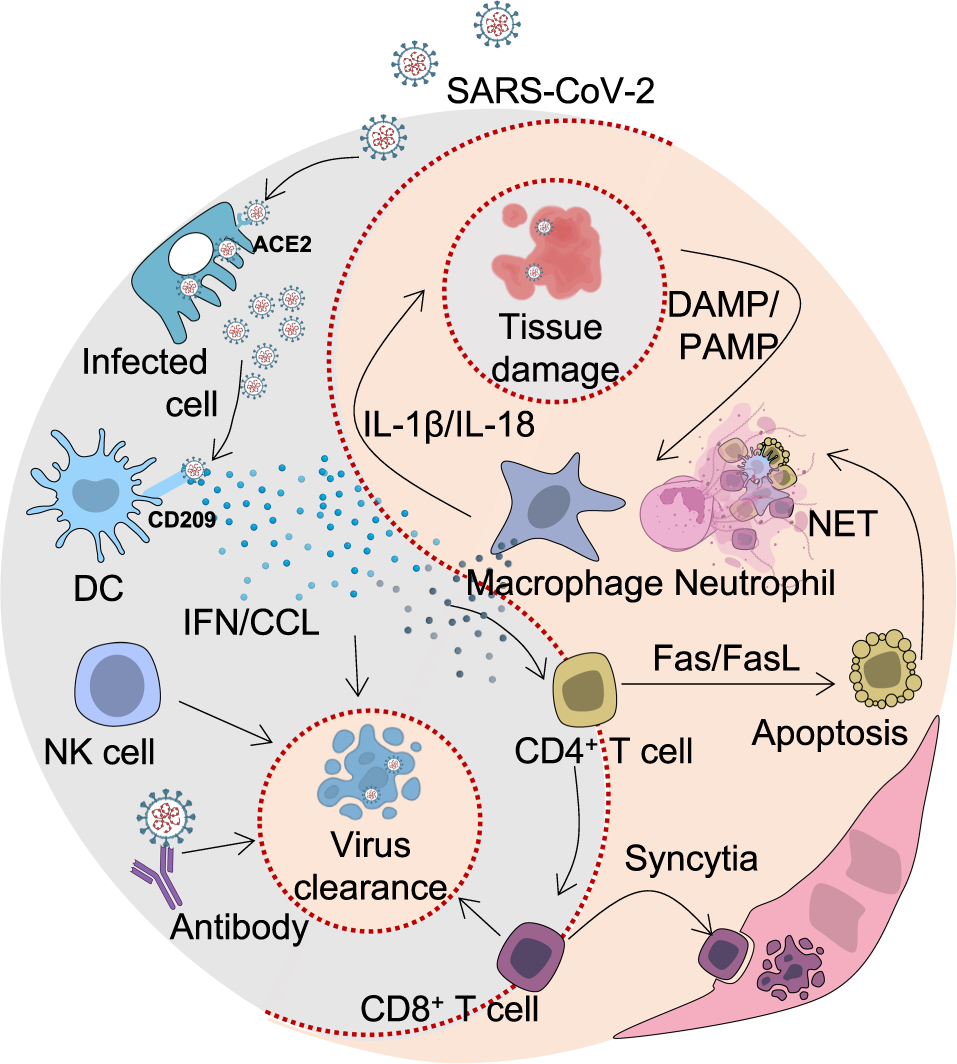
Immune response in COVID-19: what is next?
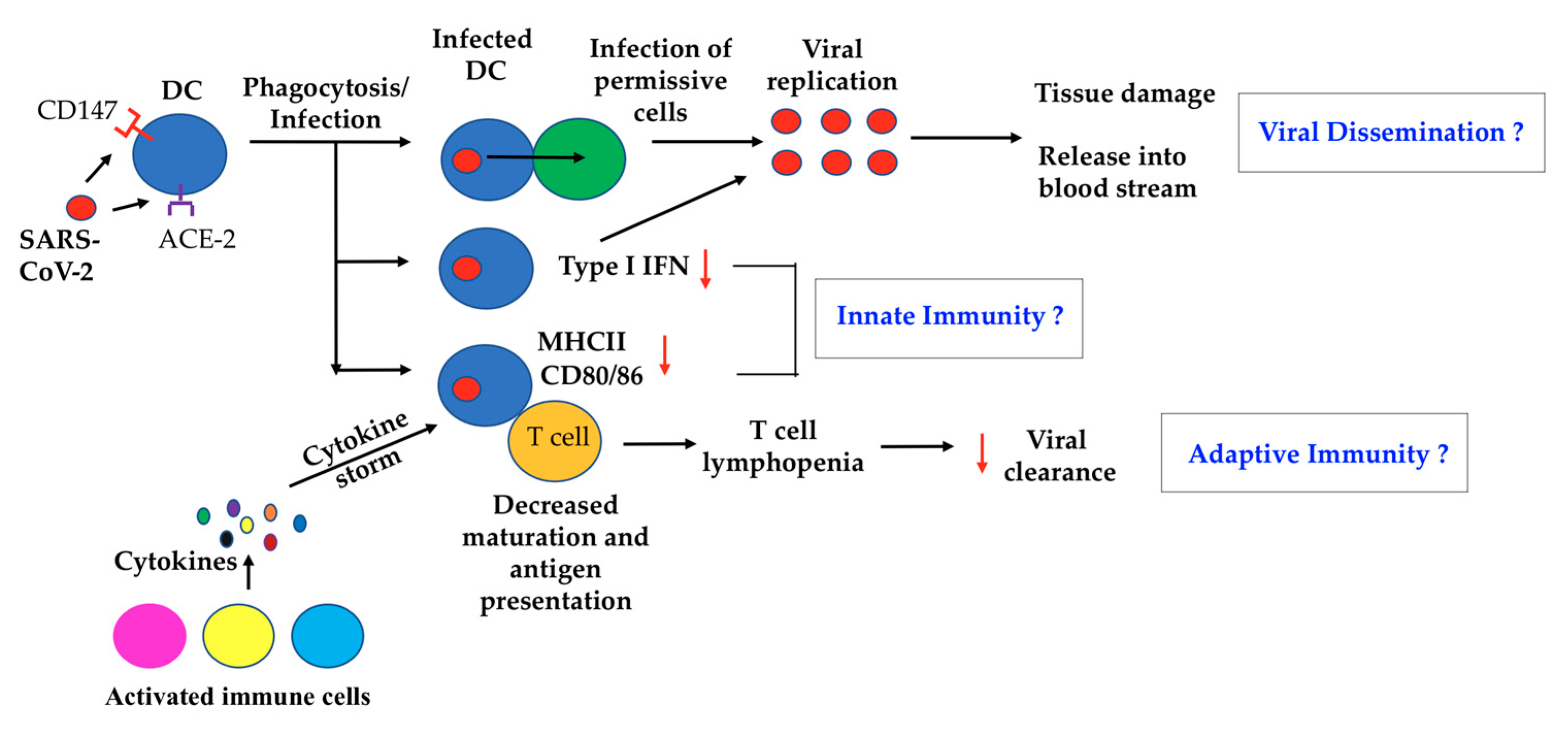
IJMS, Free Full-Text

The battle between host and SARS-CoV-2: Innate immunity and viral evasion strategies: Molecular Therapy
DC/L-SIGN recognition of spike glycoprotein promotes SARS-CoV-2 trans-infection and can be inhibited by a glycomimetic antagonist
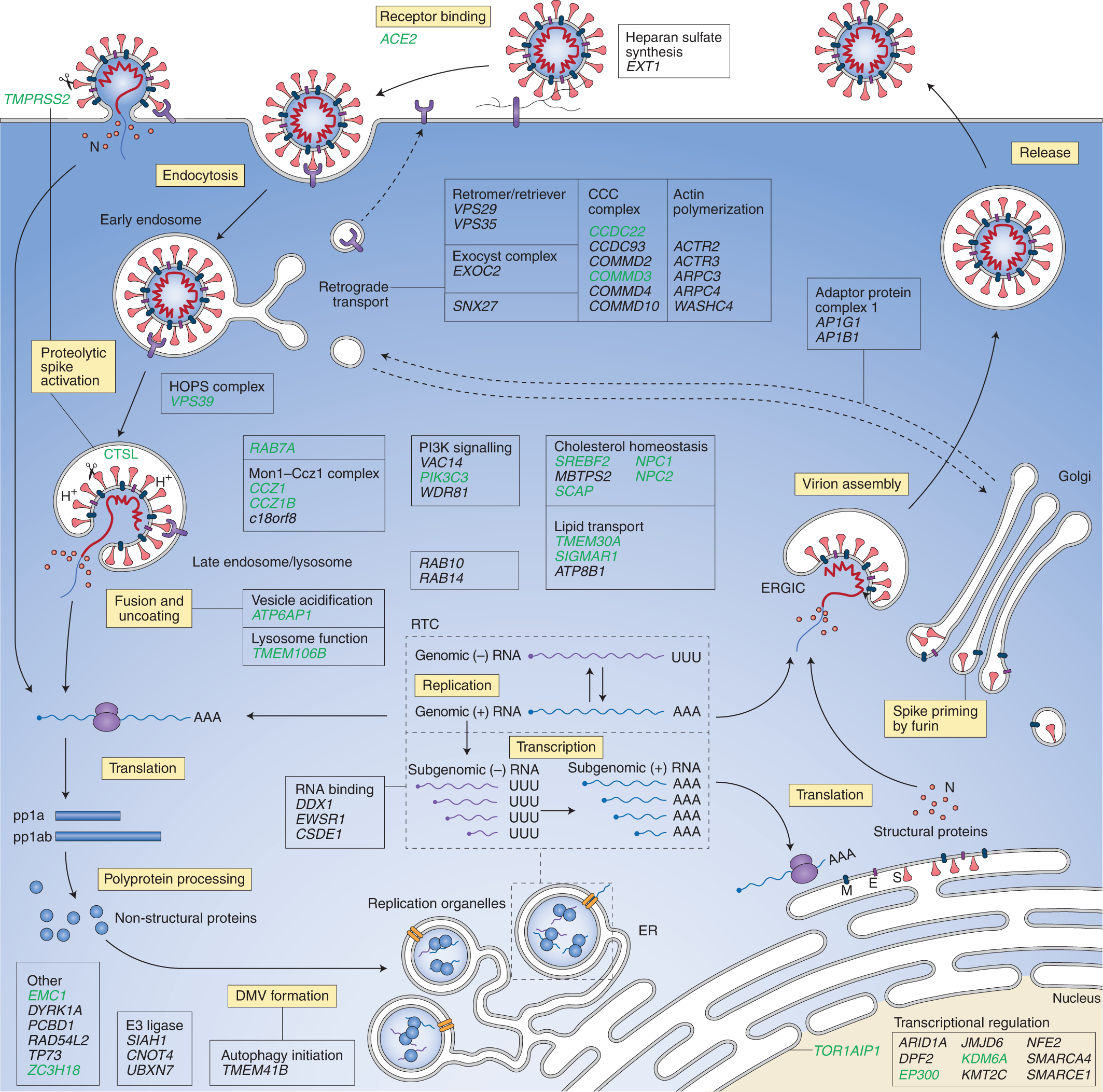
Cellular host factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection

CD209L/L-SIGN and CD209/DC-SIGN Act as Receptors for SARS-CoV-2

Innate immunity during SARS‐CoV‐2: evasion strategies and activation trigger hypoxia and vascular damage - Amor - 2020 - Clinical & Experimental Immunology - Wiley Online Library

Membrane lectins enhance SARS-CoV-2 infection and influence the neutralizing activity of different classes of antibodies

Epigenetic glycosylation of SARS-CoV-2 impact viral infection through DC&L-SIGN receptors - ScienceDirect
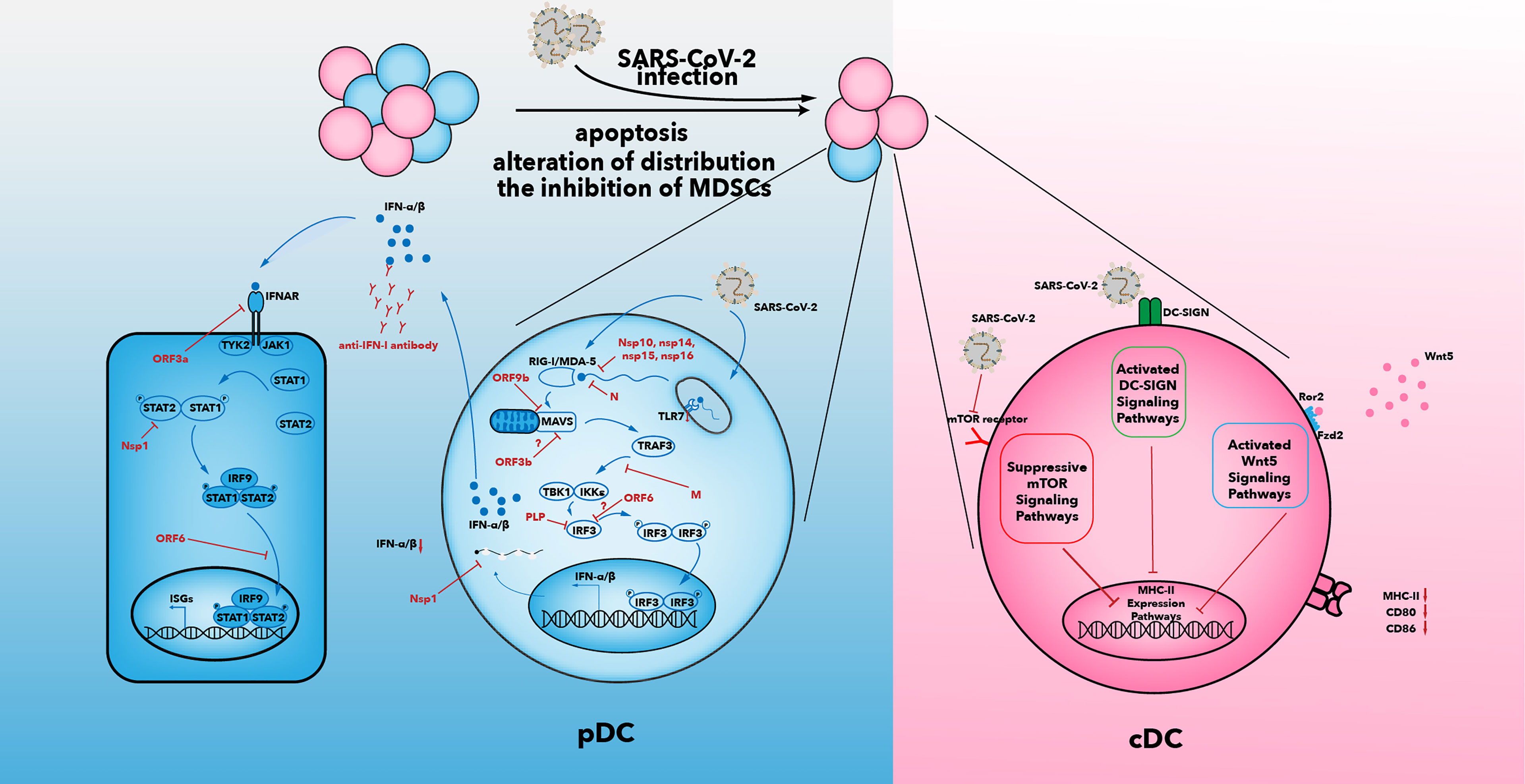
Frontiers Depletion and Dysfunction of Dendritic Cells: Understanding SARS -CoV-2 Infection

CD209L (L-SIGN) is a receptor for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus
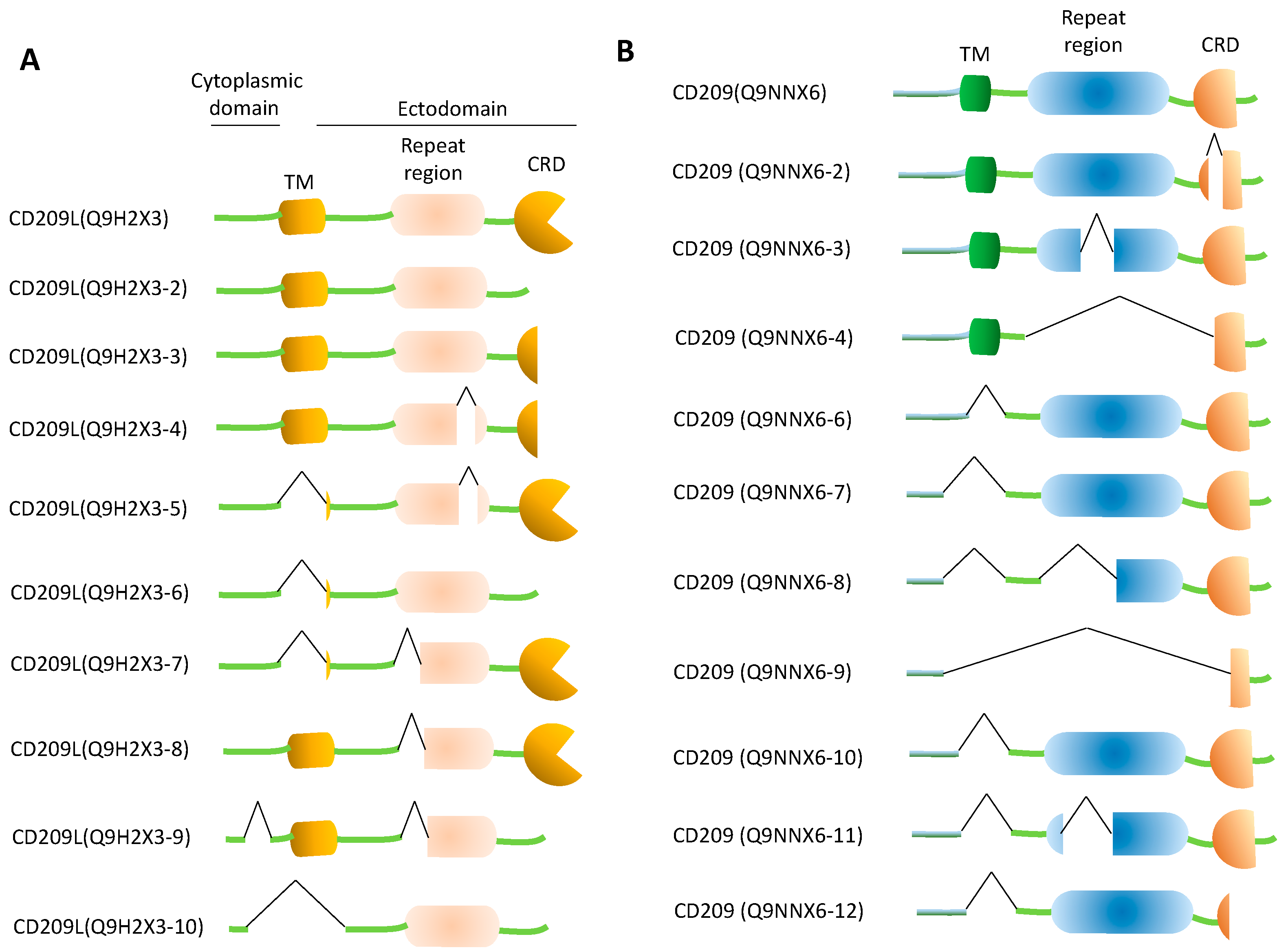
Biology, Free Full-Text
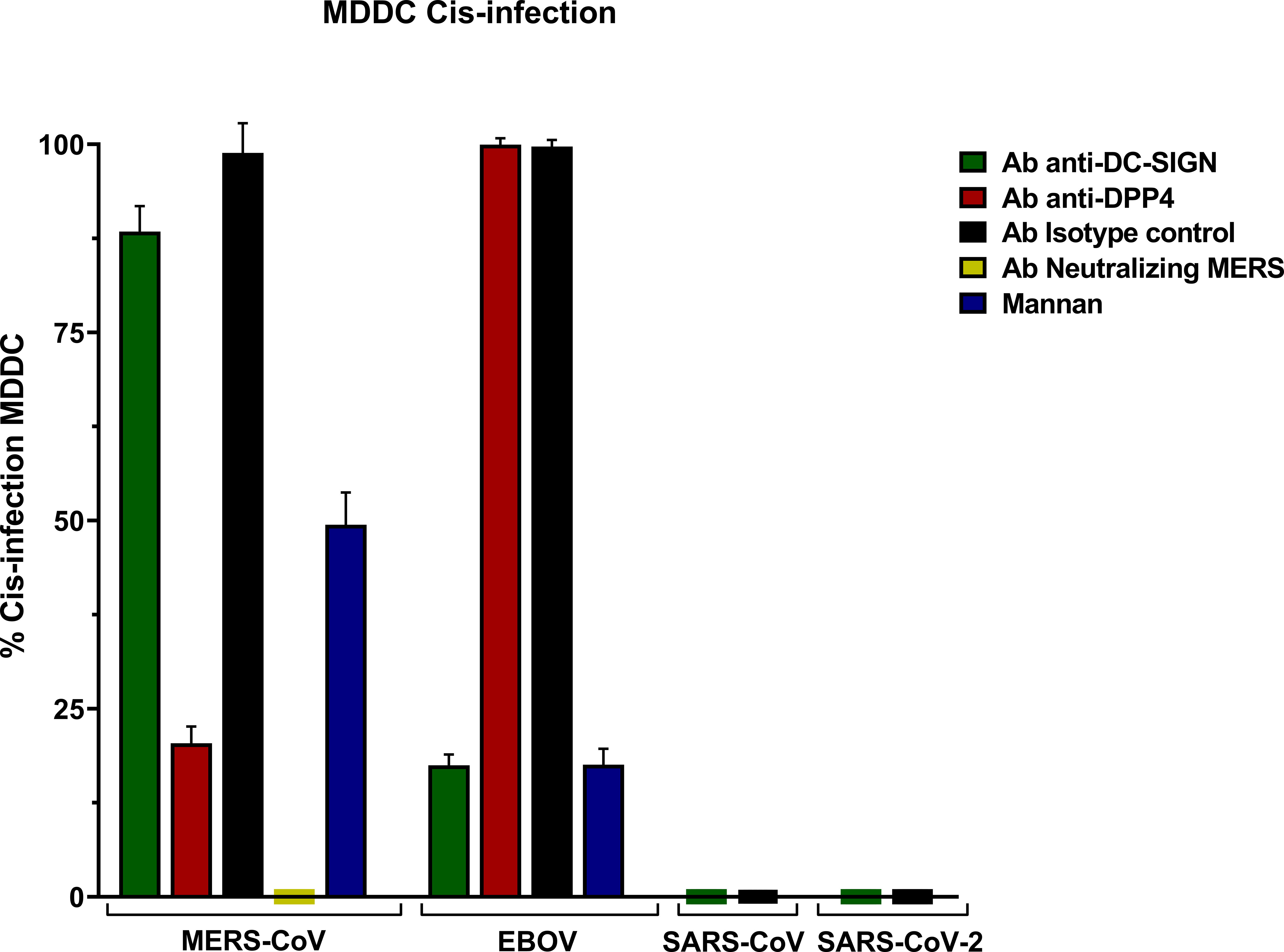
Frontiers The role of DC-SIGN as a trans-receptor in infection by MERS-CoV
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)