Relative Uptake, Metabolism, and β-Receptor Binding of (1R,2S)-4
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
The objective of the study was to compare relative uptake, metabolism, and β-receptor affinity of the new positron-emitting uptake-1 tracer (1 R ,2 S )-4-18F-fluorometaraminol (4-FM) with those of the SPECT pharmaceutical meta-123I-iodobenzylguanidine (MIBG) in Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats and spontaneously hypertensive (SHR) rats. Methods: No-carrier-added 4-18F-FM was applied to SHR and WKY rats in vivo and to retrogradely perfused hearts in vitro. Cardiac and extracardiac distribution was assessed, and metabolite formation was determined by thin-layer chromatography. The in vivo experiments were repeated with no-carrier-added 123I-MIBG. By means of autoradiography, the β-receptor affinity of 4-FM was compared with that of MIBG and propranolol (10 μmol/L) through displacement of 125I-iodocyanopindolol (1.5 pmol/L) in slices of heart and spleen. Results: Cardiomyopathic hearts showed heterogeneous 4-18F-FM uptake with gradients up to 3.6 in vivo and in vitro between different regions of the heart. Control hearts showed such gradients in 4-18F-FM uptake only in vitro. 123I-MIBG exhibited a less heterogeneous in vivo distribution in SHR hearts. Extracardiac differences between WKY and SHR were found for uptake of 4-18F-FM in the spleen (63.3% ± 4% vs. 38.8% ± 5.7% of cardiac activity) and for renal uptake of 123I-MIBG (373% ± 27% vs. 81.4% ± 17% of cardiac activity). Metabolites of 4-18F-FM were found only in the liver and those of 123I-MIBG were found in the liver and kidney with a nearly equal relative fraction in both types of animals of about 20%, 60%, and 30%, respectively. 4-FM suppressed cardiac-specific β-receptor binding of 125I-iodocyanopindolol in heart and spleen of both types of animals significantly, whereas MIBG had almost no effect. Conclusion: The more heterogeneous cardiac distribution of 4-18F-FM suggests that it reflects alterations in uptake-1 better than 123I-MIBG in addition to the possibility of quantification and higher spatial resolution by PET compared with SPECT. Altered biotransformation in cardiomyopathic diseases may also impair the evaluation of 123I-MIBG-SPECT data. The β-receptor binding of 4-18F-FM must be further elucidated.
IJMS, Free Full-Text
Frontiers Immune Metabolism of IL-4-Activated B Cells and Th2 Cells in the Context of Allergic Diseases

Full article: Pathogenicity and virulence of West Nile virus revisited eight decades after its first isolation

Insights Into Mechanisms of GDF15 and Receptor GFRAL: Therapeutic Targets: Trends in Endocrinology & Metabolism
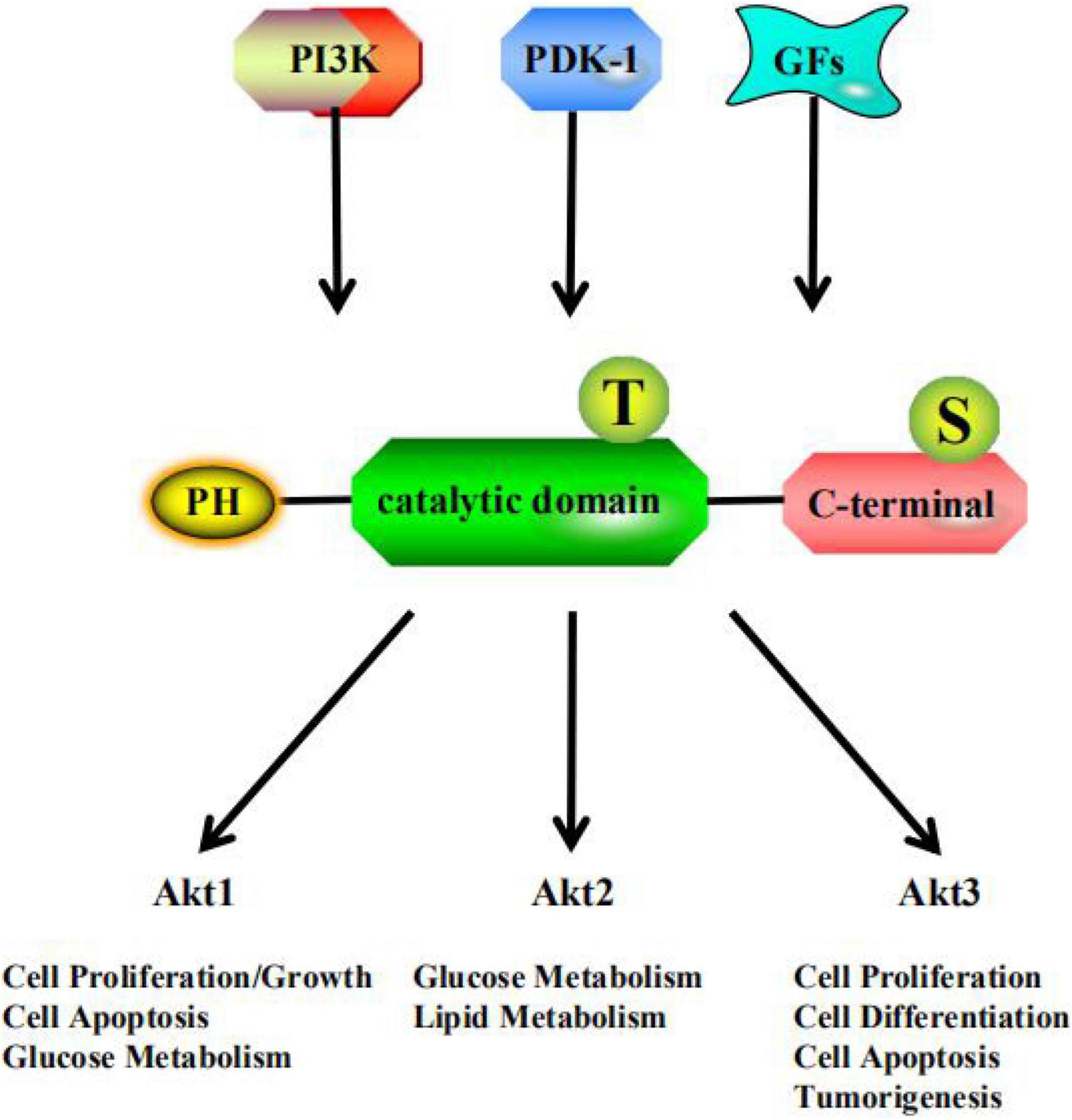
Frontiers Akt: A Potential Drug Target for Metabolic Syndrome
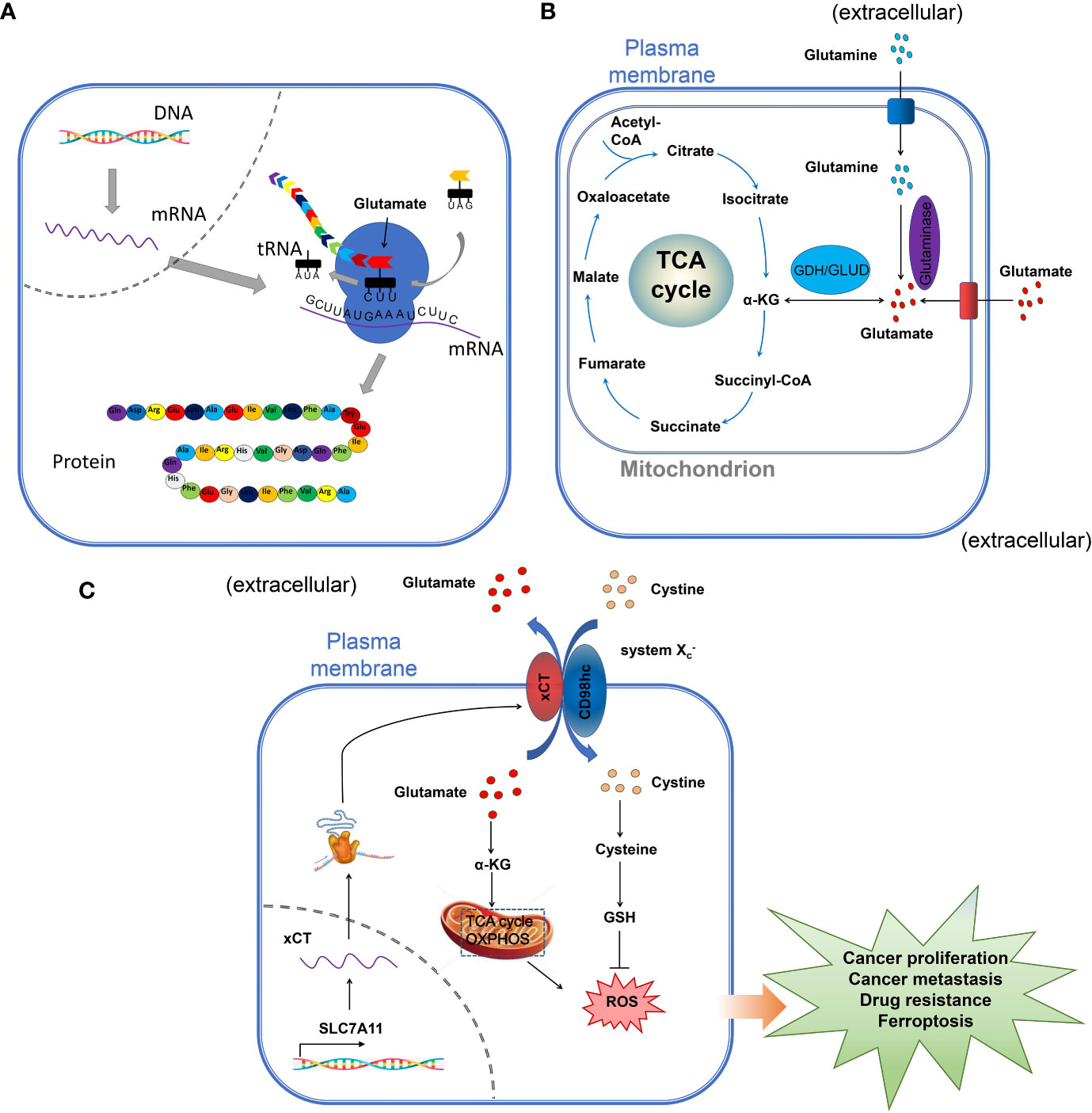
Frontiers The role of glutamate receptors in the regulation of the tumor microenvironment

Untangling the effect of insulin action on brain mitochondria and metabolism - Schell - 2021 - Journal of Neuroendocrinology - Wiley Online Library
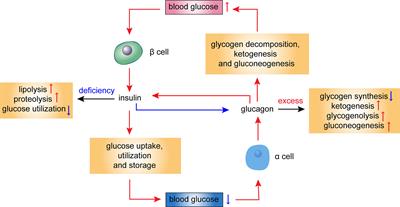
Frontiers Role of Glucagon and Its Receptor in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes
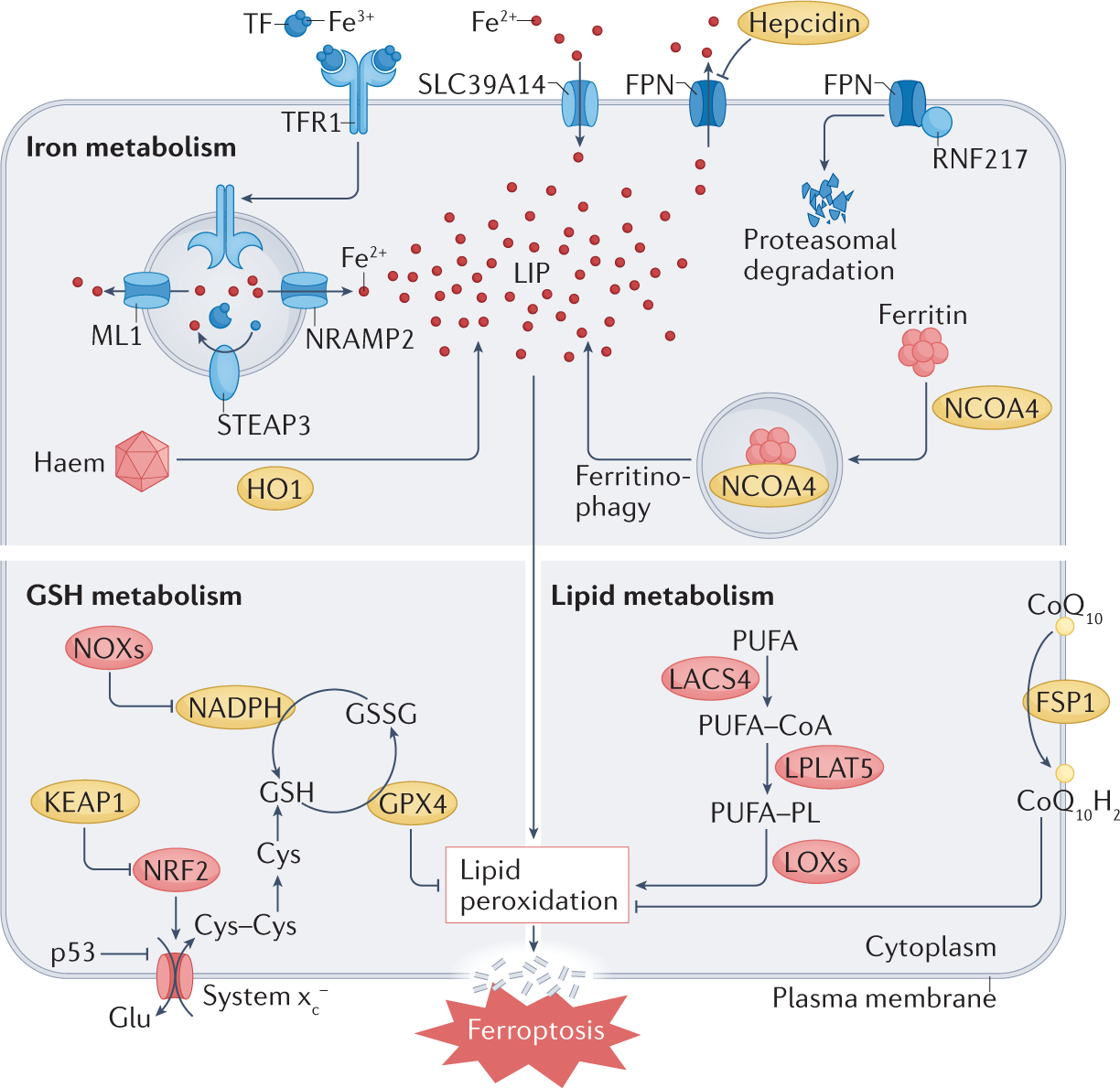
The molecular and metabolic landscape of iron and ferroptosis in cardiovascular disease

PHLPP1 promotes neutral lipid accumulation through AMPK/ChREBP-dependent lipid uptake and fatty acid synthesis pathways - ScienceDirect

Mechanisms of muscle insulin resistance and the cross‐talk with liver and adipose tissue - Silva Rosa - 2020 - Physiological Reports - Wiley Online Library
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







