Rapid Redox Cycling of Fe(II)/Fe(III) in Microdroplets during Iron
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição

Raw EDB experimental data for a Fe III (Cit)/CA (molar ratio of 0.05)

Rapid Iron Reduction Rates Are Stimulated by High-Amplitude Redox Fluctuations in a Tropical Forest Soil
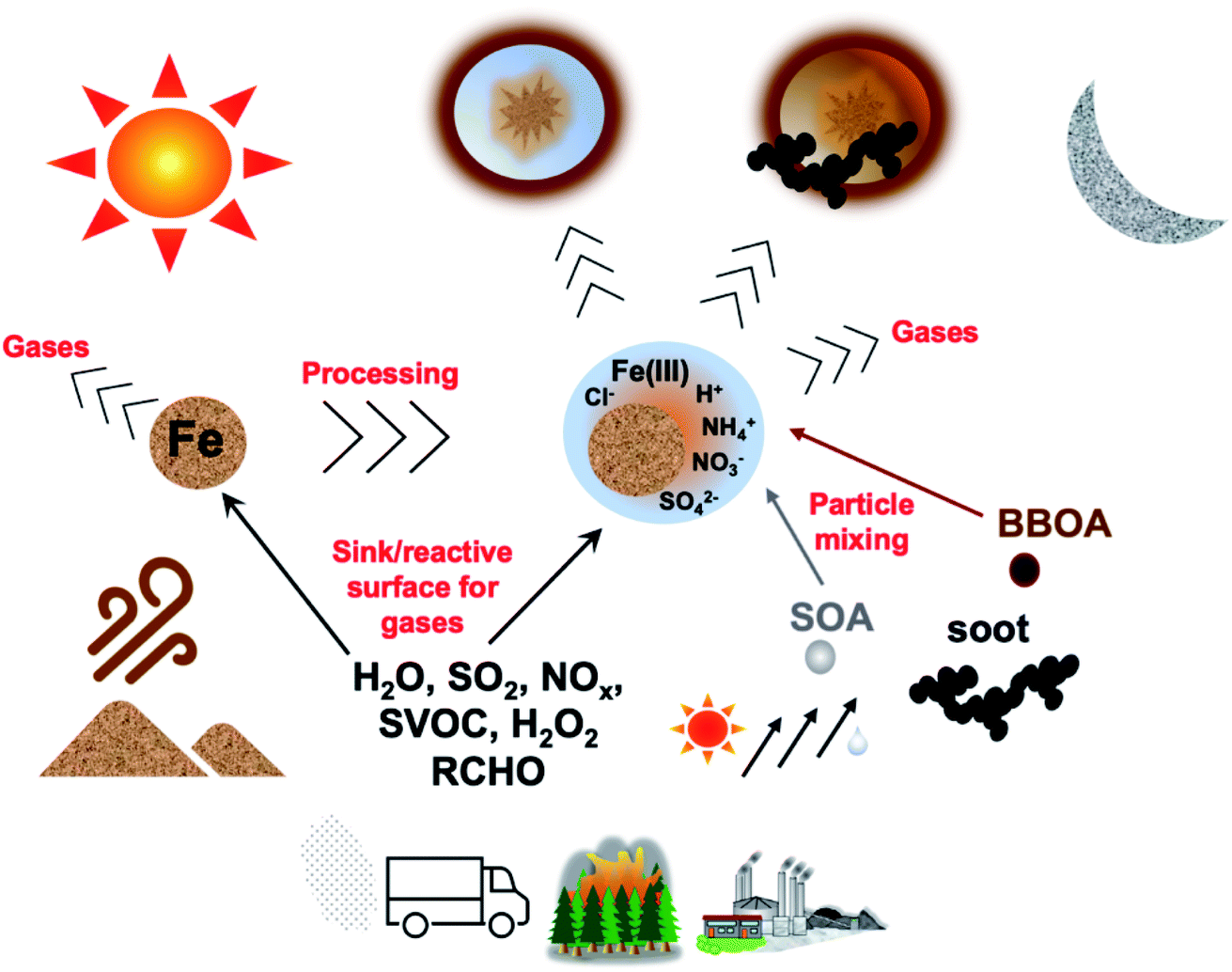
A perspective on iron (Fe) in the atmosphere: air quality, climate, and the ocean - Environmental Science: Processes & Impacts (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D2EM00176D

New Insight toward Synergetic Effect for Platinum Recovery Coupling with Fe( III)-Oxalate Complexes Degradation through Photocatalysis
a) Fe III (Cit) / CA (molar ratio 0.05) particle mass change with

Nitrite/Nitrous Acid Generation from the Reaction of Nitrate and Fe(II) Promoted by Photolysis of Iron–Organic Complexes
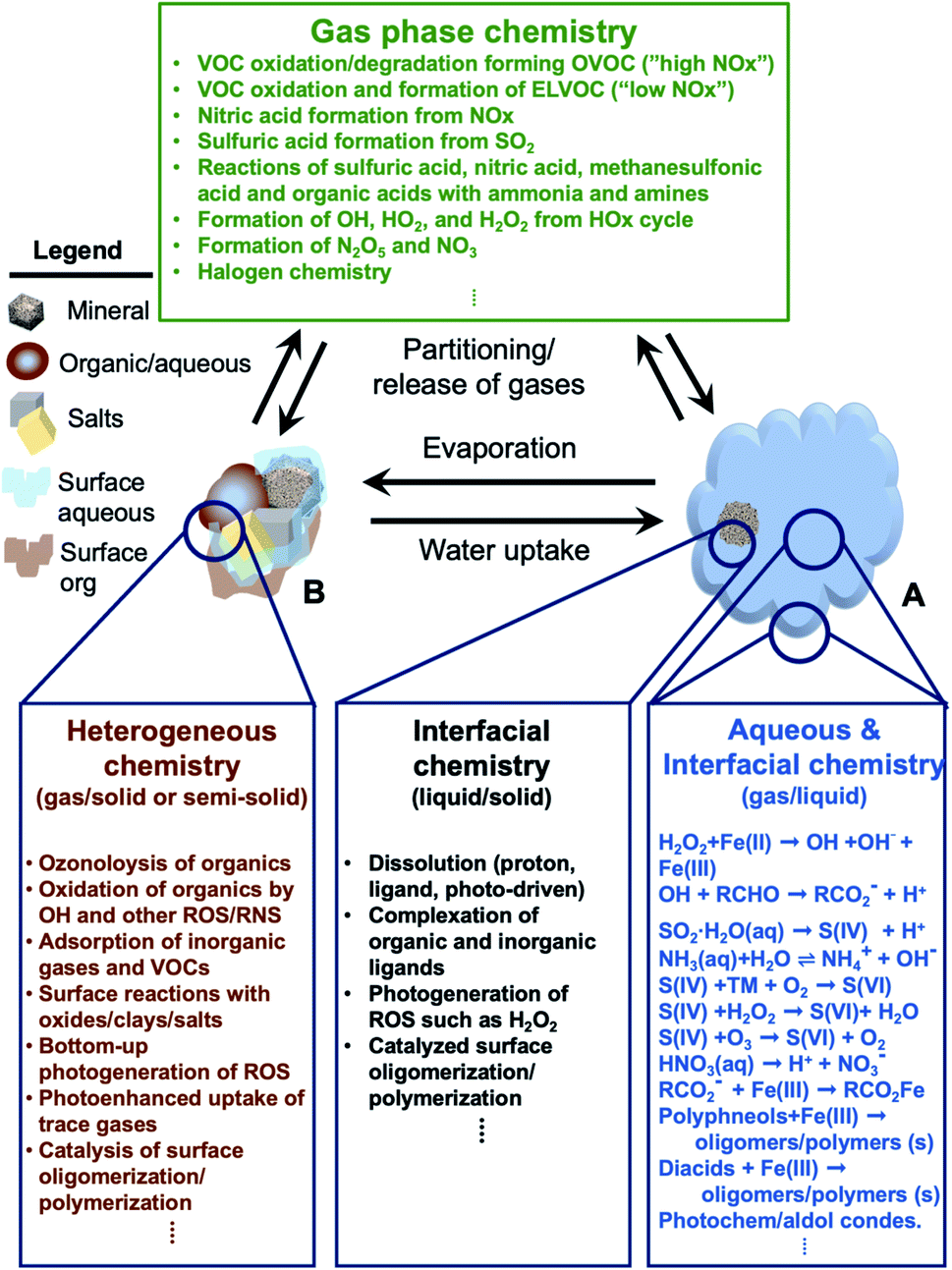
Aging of atmospheric aerosols and the role of iron in catalyzing brown carbon formation - Environmental Science: Atmospheres (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1EA00038A

Photochemical Cycling of Iron Mediated by Dicarboxylates: Special Effect of Malonate

Consecutive Fe redox cycles decrease bioreducible Fe(III) and Fe isotope fractionations by eliminating small clay particles - ScienceDirect

Redox cycling of Fe(II) and Fe(III) in magnetite accelerates aceticlastic methanogenesis by Methanosarcina mazei - Wang - 2020 - Environmental Microbiology Reports - Wiley Online Library

Rapid Iron Reduction Rates Are Stimulated by High-Amplitude Redox Fluctuations in a Tropical Forest Soil

Significantly Accelerated Hydroxyl Radical Generation by Fe(III)–Oxalate Photochemistry in Aerosol Droplets
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)