Pathogens, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
In 1973, the National Rabies Program was created in Brazil through an agreement between the Ministry of Health and Agriculture. Since its beginning, it developed integrated action through access to free post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) for people at risk, dog vaccination campaigns, a joint surveillance system, and awareness. This study aims to describe human rabies in Brazil under the One Health perspective in recent decades, including achievements in the control of dog-mediated cases and challenges in human cases transmitted by wild animals. This paper also explores possible drivers of human rabies in the Northeast Region with half of the cases. The first part of this study was descriptive, presenting data and examples by periods. Statistical analysis was performed in the last period (2010–2022) to explore possible drivers. Dog-mediated human cases decreased from 147 to 0, and dog cases decreased from 4500 to 7. A major challenge is now human cases transmitted by wild animals (bats, non-human primates, and wild canids). Most current human cases occur in municipalities with a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forest biome and a Gini index higher than 0.5. In the multivariable analysis, an association with temperature was estimated (OR = 1.739; CI95% = 1.181–2.744), and primary healthcare coverage (OR = 0.947; CI95% = 0.915–0.987) was identified as a protector. It is possible to significantly reduce the number of dog-mediated human rabies cases through the efforts presented. However, Brazil has wildlife variants of the rabies virus circulating. The association of human cases with higher temperatures in the Northeast is a concern with climate change. To reduce human cases transmitted by wild animals, it is important to continue distributing free PEP, especially in remote at-risk areas in the Region, and to increase awareness.

A Dietary Fiber-Deprived Gut Microbiota Degrades the Colonic Mucus Barrier and Enhances Pathogen Susceptibility: Cell
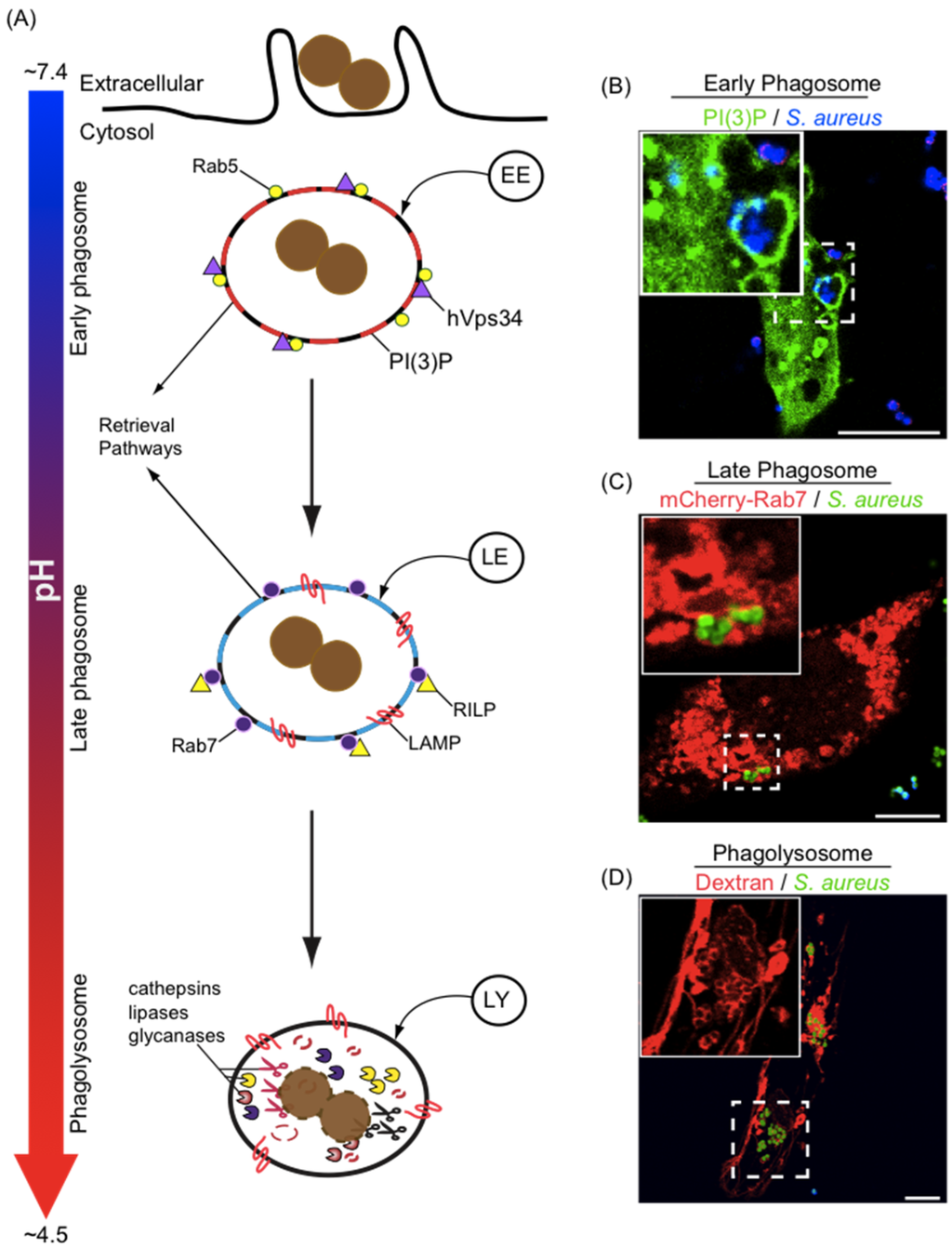
Pathogens, Free Full-Text

Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 - The Lancet
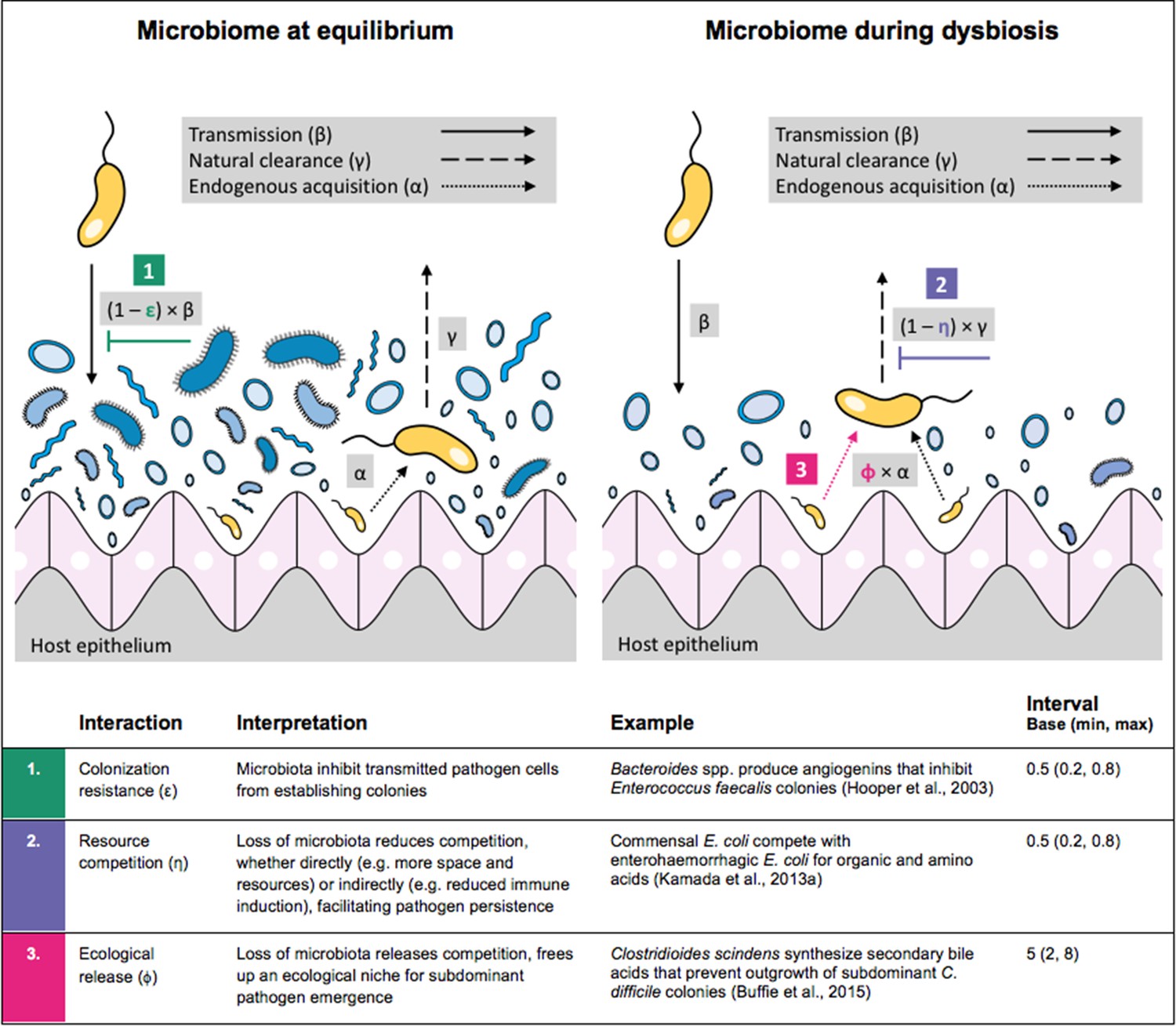
Microbiome-pathogen interactions drive epidemiological dynamics of antibiotic resistance: A modeling study applied to nosocomial pathogen control
Foodborne Pathogens and Disease Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers

NADases as weapons for both plant pathogens and their hosts

Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 - The Lancet
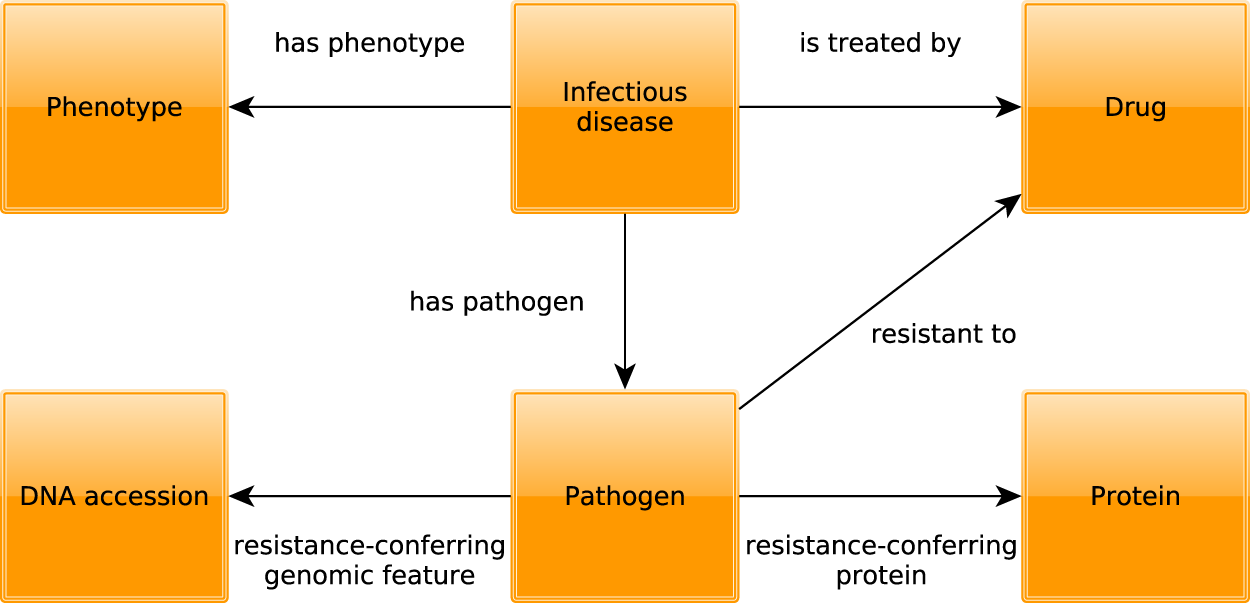
PathoPhenoDB, linking human pathogens to their phenotypes in support of infectious disease research

Pathogens Packet - Bacteria Viruses Protozoa Fungi Parasites and Prions - Homeschool Den

Microbial Minimalism: Genome Reduction in Bacterial Pathogens - ScienceDirect

Effect of sequential UV/free chlorine disinfection on opportunistic pathogens and microbial community structure in simulated drinking water distribution systems - ScienceDirect
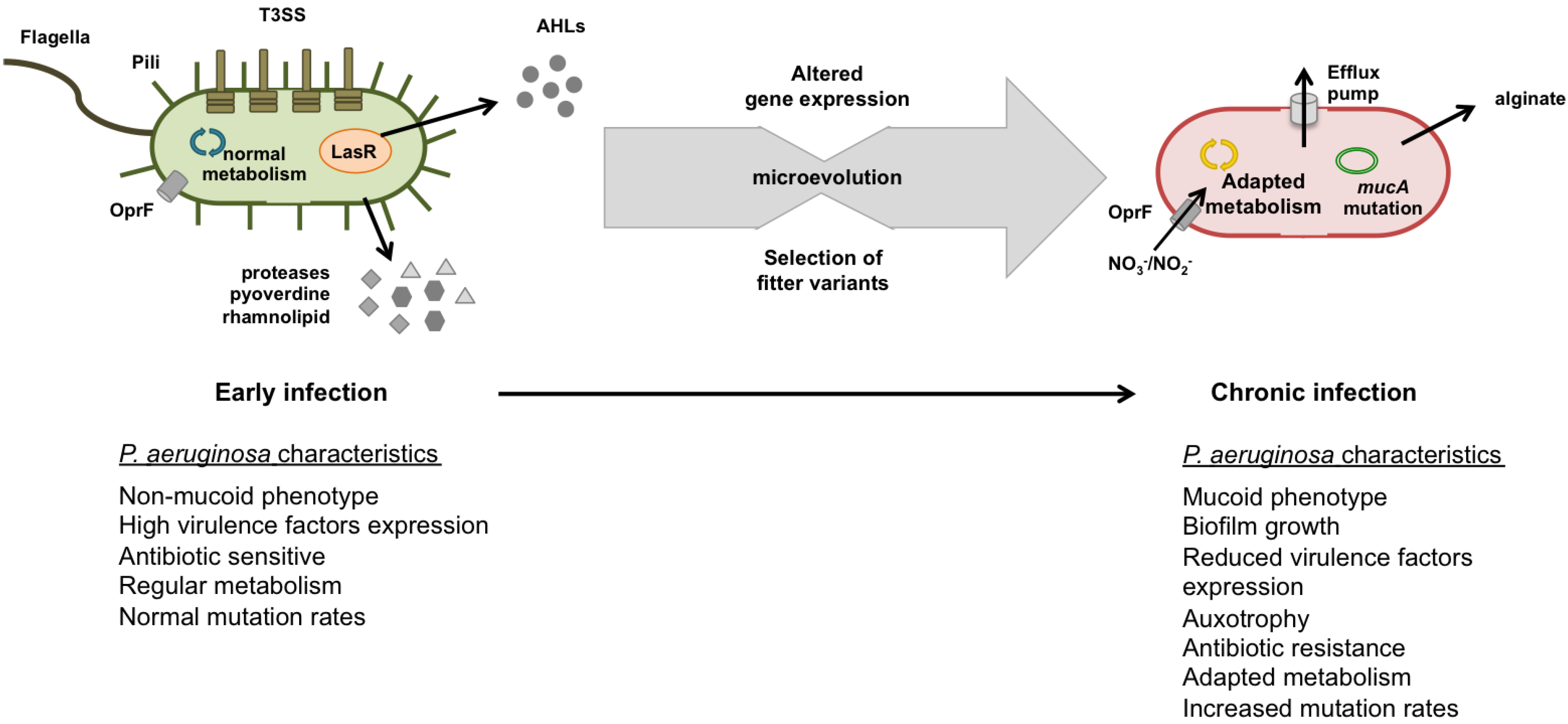
Pathogens, Free Full-Text
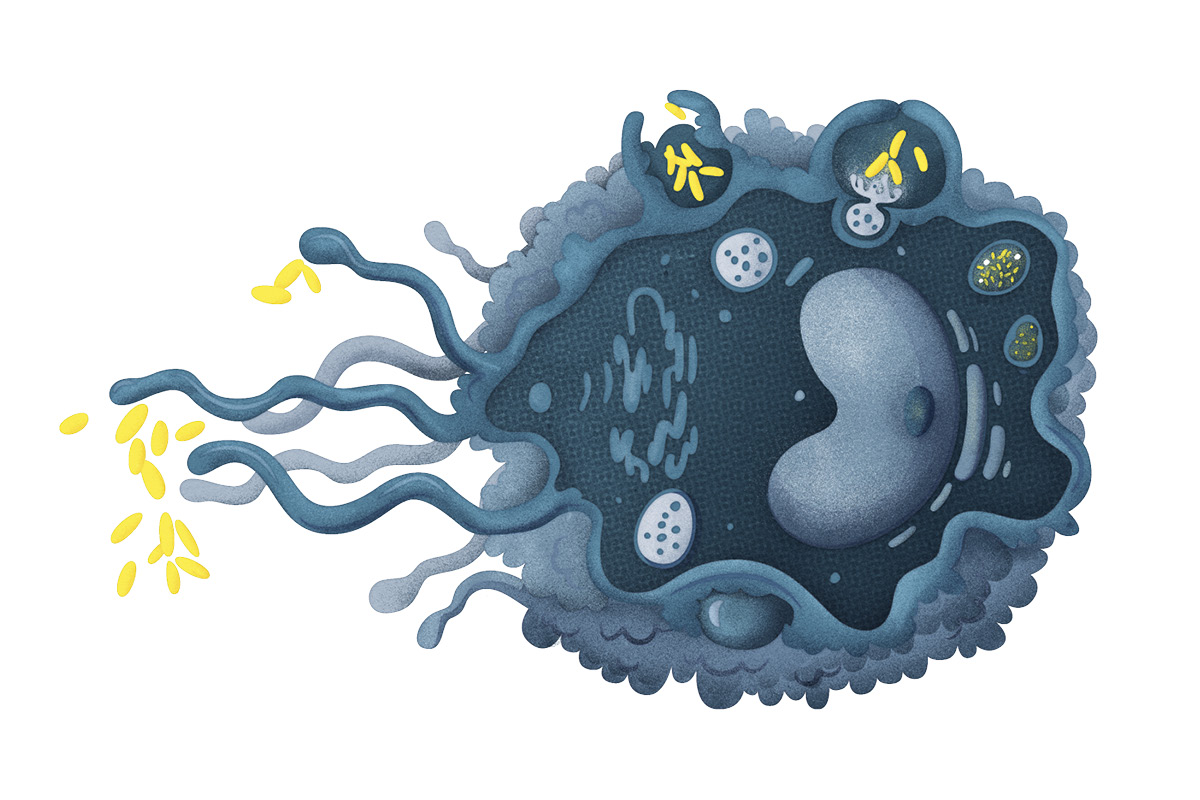
Macrophages: What are they and how do they kill bacteria? - BBC Science Focus Magazine
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)


/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2023/x/n/mH2C8CQpavPAb5sbiD9A/gabriel-ruiz-1.jpeg)




