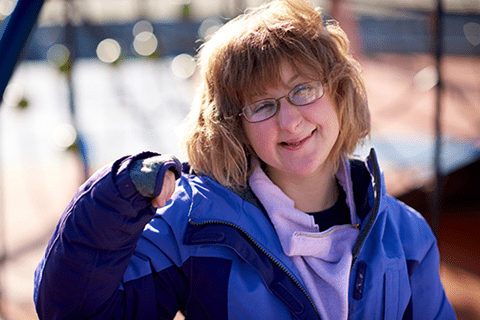PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
A typical six-month-old girl with Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome was presented with typical facial changes including downward-sloping palpebral fissures, prominent forehead, hypertelorism, limited mouth opening, large beaked nose, and high arched palate. Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome (RTS) was first described by Michail et al[1] and subsequently by Rubinstein and Taybi[2]. We present a typical six-month-old girl with RTS. Her mother had ovarian cancer and polyhydramnios during the pregnancy. Parents are closely related. There were frequent respiratory infections resulting in two hospital admissions. Physical examination revealed typical facial changes including downward-sloping palpebral fissures, prominent forehead, hypertelorism, limited mouth opening, large beaked nose, and high arched palate (Fig. 1). A history of increased tearing was compatible with nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Other features include general hypotonia with delayed developmental milestones, short and broad thumbs and toes (Fig. 1). Chest x-ray showed cardiomegaly (Fig. 2). She had normal karyotype.
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.ahajournals.org/cms/asset/b5e0a34d-a621-4a1d-b072-63c7222dc31a/jah37672-fig-0006.png)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus: A Contemporary Perspective for the Pediatric and Adult Cardiac Care Provider
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://media.springernature.com/m685/springer-static/image/art%3A10.1038%2Fs41372-019-0506-7/MediaObjects/41372_2019_506_Fig6_HTML.png)
Patent ductus arteriosus in preterm infants: is early transcatheter closure a paradigm shift?
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.mdpi.com/jpm/jpm-13-01263/article_deploy/html/images/jpm-13-01263-g001.png)
JPM, Free Full-Text
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.ahajournals.org/cms/asset/6af36fb1-bcda-43f2-8246-33eab0b9eadd/hc2392821002.jpeg)
Char Syndrome, an Inherited Disorder With Patent Ductus Arteriosus, Maps to Chromosome 6p12-p21
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://assets.aboutkidshealth.ca/akhassets/Patent_ductus_arteriosus_XRAY_MEDIMG_PHO_EN.png?RenditionID=19)
Diagnosis of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in premature babies
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.chop.edu/sites/default/files/patent-ductus-arteriosus-treatment-illustration-272px.png)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://i1.rgstatic.net/ii/profile.image/926912121675782-1598004479904_Q64/Ehsan-Aghaei-Moghadam.jpg)
PDF) Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1875213610001555-gr2.jpg)
The ductus arteriosus: Physiology, regulation, and functional and congenital anomalies - ScienceDirect
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Patrick-Mcnamara-14/publication/324968903/figure/fig9/AS:963235951943683@1606664755233/A-and-B-Angiographic-still-frames-in-lateral-projection-of-the-patent-ductus_Q320.jpg)
PDF) Patent ductus arteriosus: The physiology of transition
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://ars.els-cdn.com/content/image/1-s2.0-S1058981319301821-gr2.jpg)
Transcatheter closure of patent ductus arteriosus in a tiniest baby – 510 grams - ScienceDirect
![PDF] Patent Ductus Arteriousus Device Closure in an Infant with Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome](https://europepmc.org/articles/PMC7605084/bin/PEDS_20201209_f3.jpg)
Patent Ductus Arteriosus of the Preterm Infant. - Abstract - Europe PMC
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)