Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Clinically, intrauterine hypoxia is the foremost cause of perinatal morbidity and developmental plasticity in the fetus and newborn infant. Under hypoxia, deviations occur in the lung cell epigenome. Epigenetic mechanisms (e.g., DNA methylation, histone modification, and miRNA expression) control phenotypic programming and are associated with physiological responses and the risk of developmental disorders, such as bronchopulmonary dysplasia. This developmental disorder is the most frequent chronic pulmonary complication in preterm labor. The pathogenesis of this disease involves many factors, including aberrant oxygen conditions and mechanical ventilation-mediated lung injury, infection/inflammation, and epigenetic/genetic risk factors. This review is focused on various aspects related to intrauterine hypoxia and epigenetic programming in lung development and disease, summarizes our current knowledge of hypoxia-induced epigenetic programming and discusses potential therapeutic interventions for lung disease.
Prolonged PayoffBiomedicines, Free Full-Text, global longitudinal
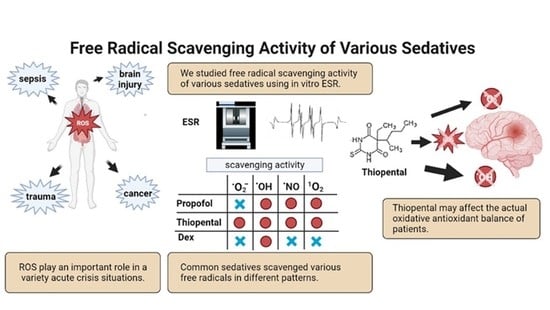
Free Radicals Brain Injury - Colaboratory
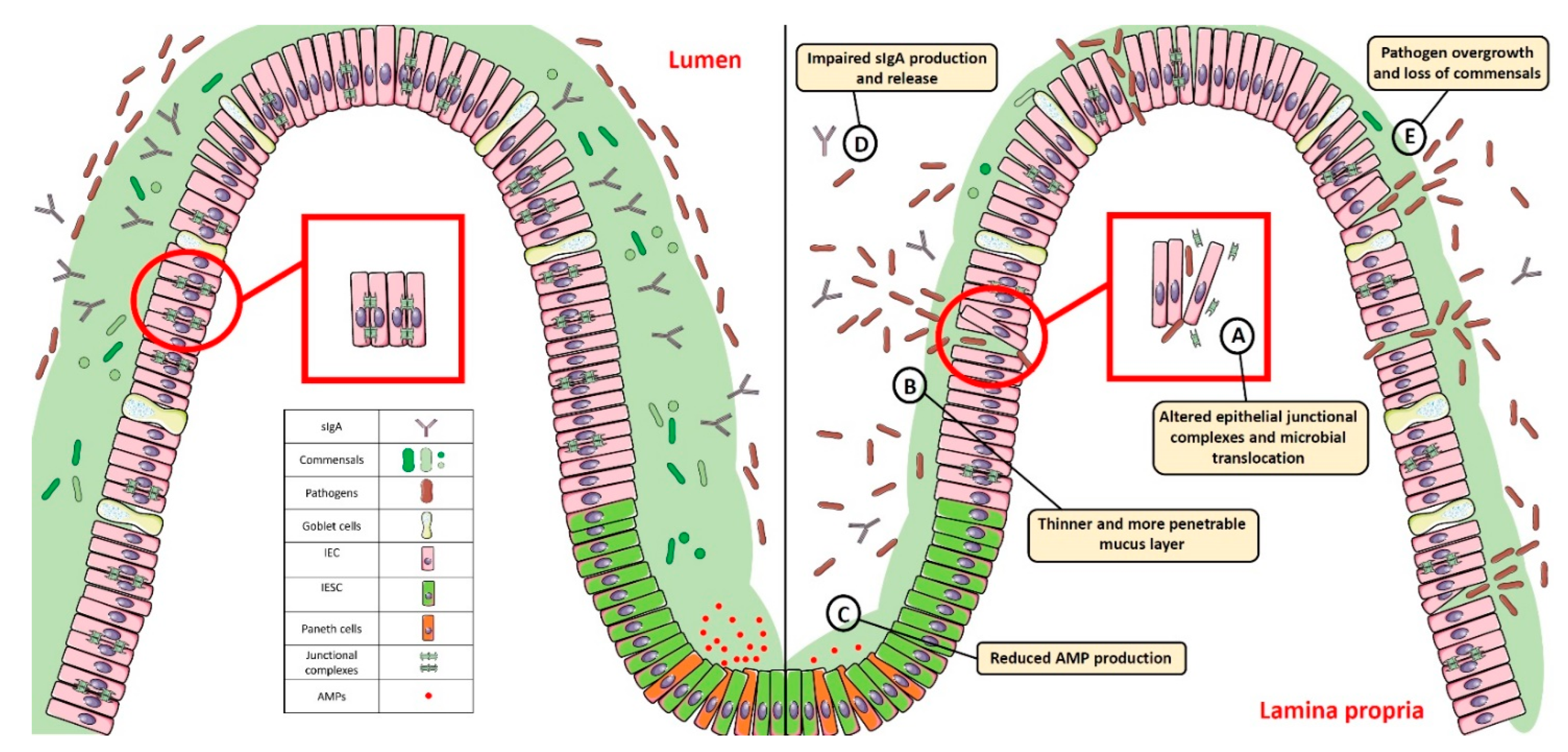
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
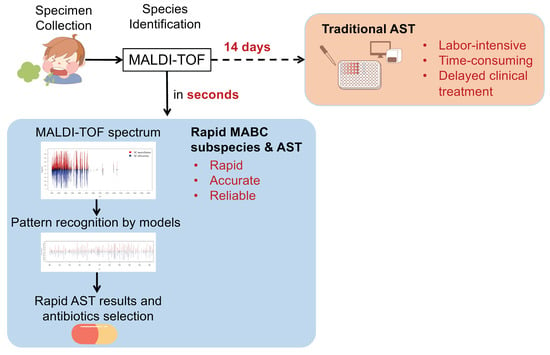
Flexanalysis 3.4 - Colaboratory

How Nanophotonic Label-Free Biosensors Can Contribute to Rapid and

Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
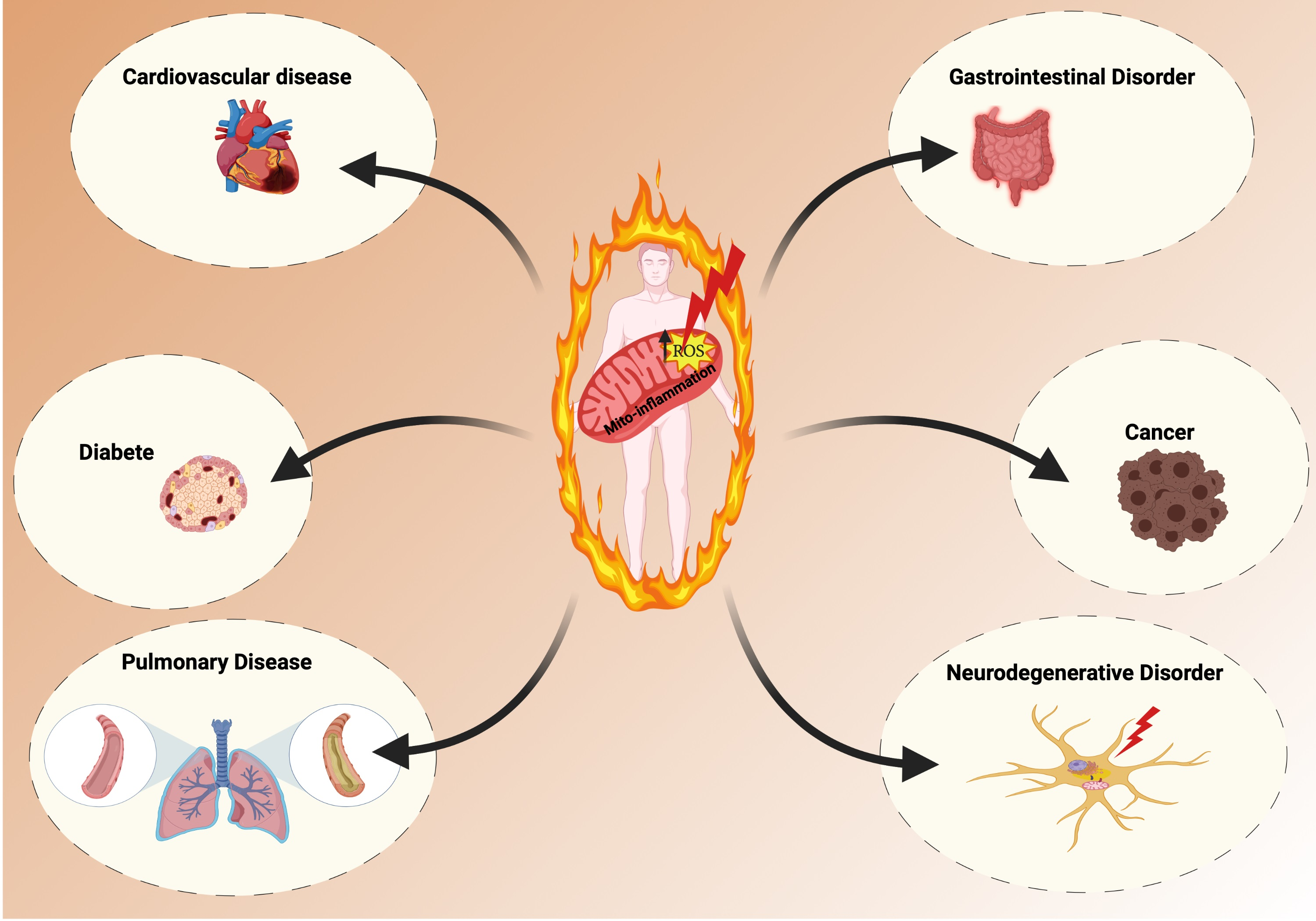
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
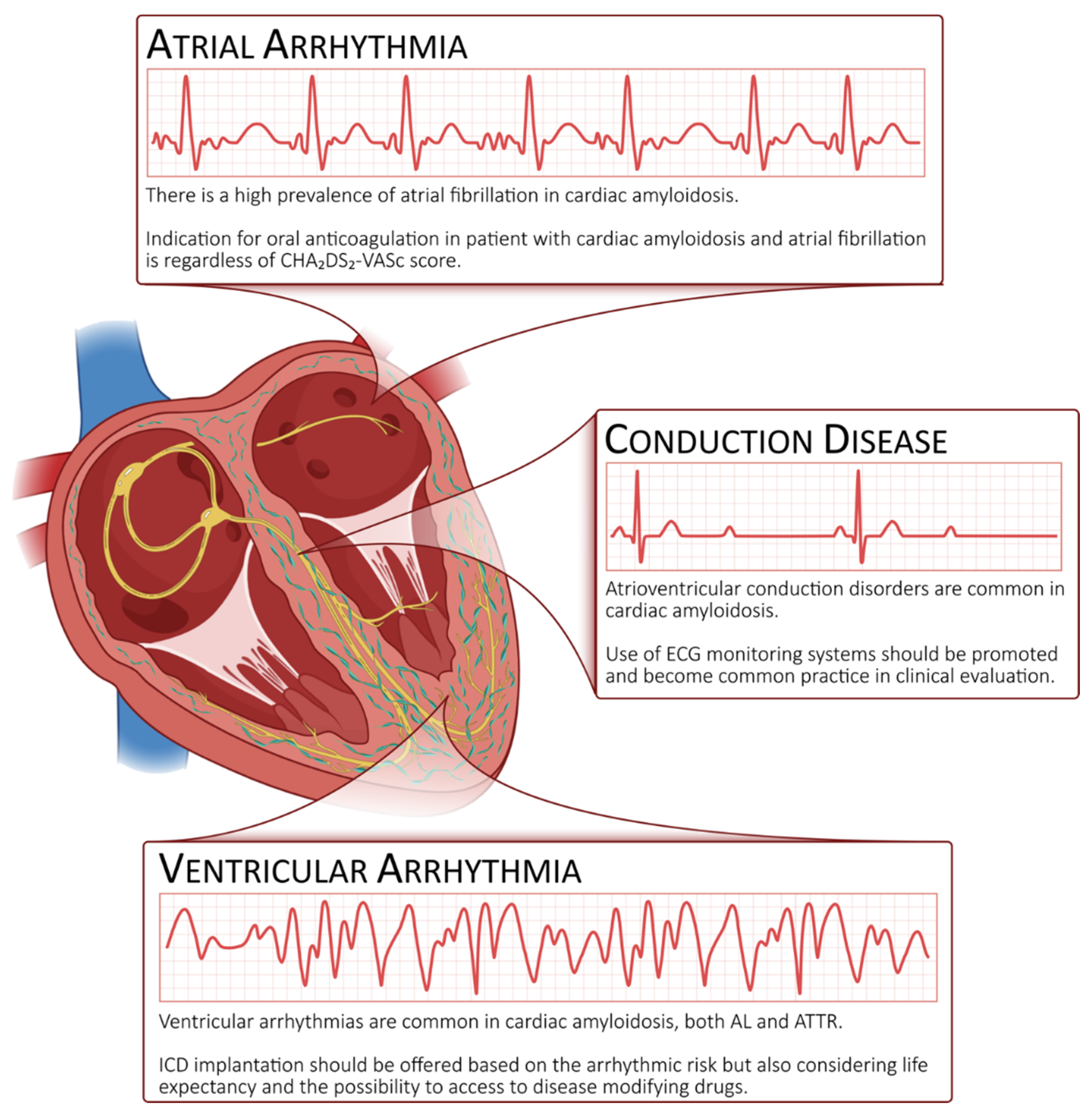
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

Long COVID: pathophysiological factors and abnormalities of
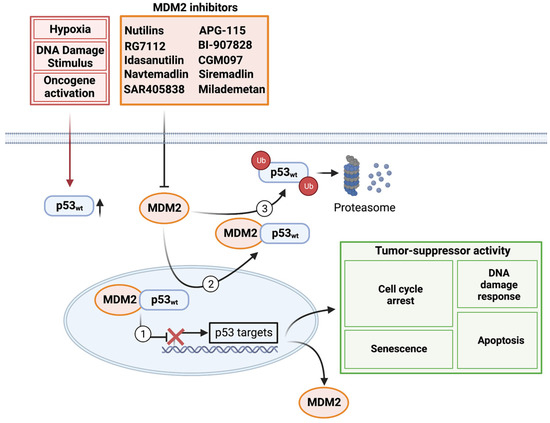
Dha 84 Form 11 Get File - Colaboratory
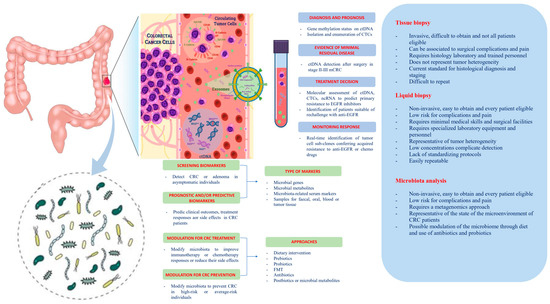
Medical Books Free Beyond Pain Moshirir - Colaboratory
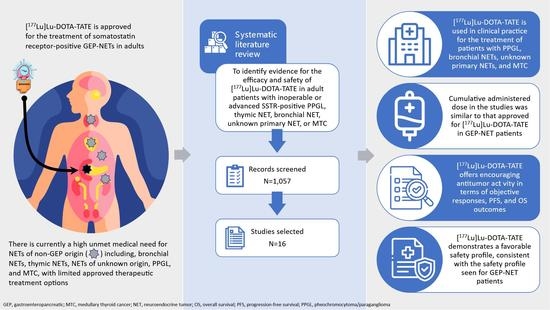
Free Of Fp Pl Pfs Installer Latest Version - Colaboratory
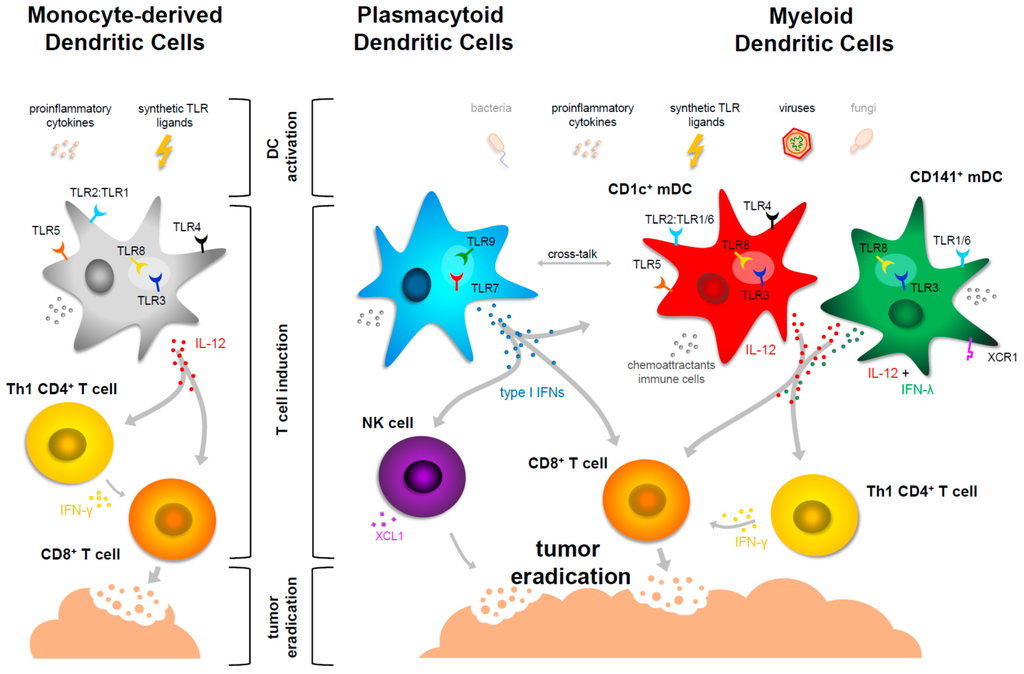
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

Gut microbiota and its metabolites in depression: from
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







